5G: Technology
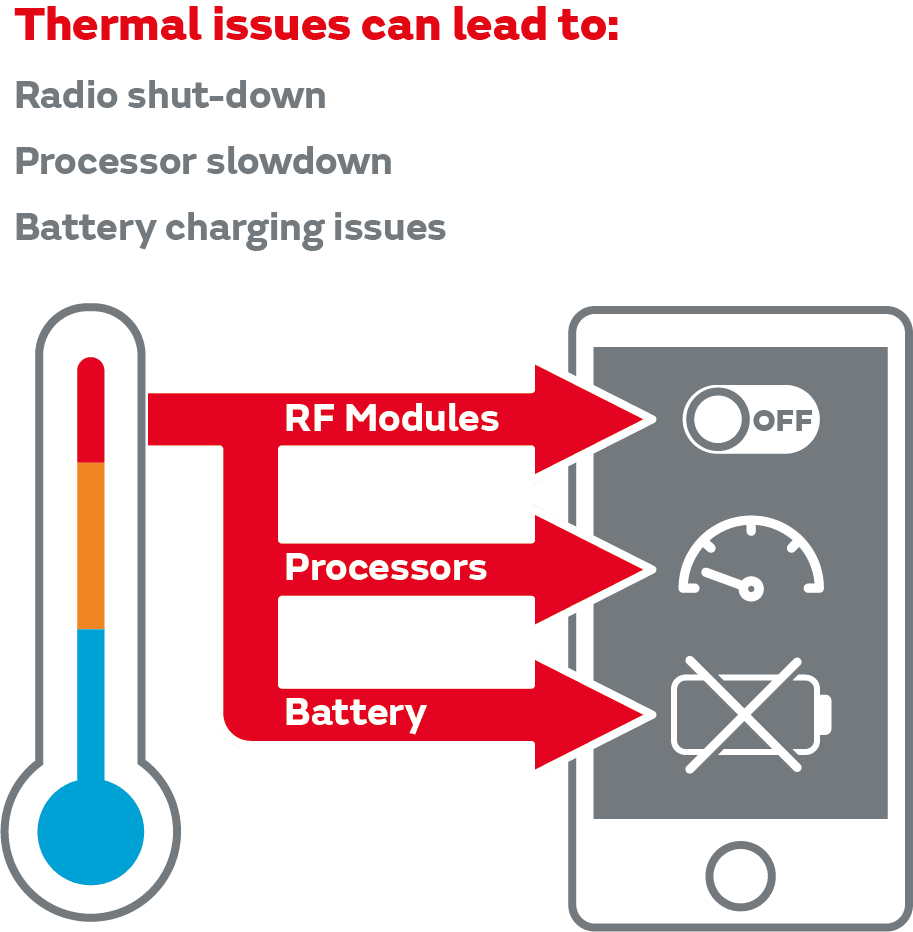
5G Challenge: Thermal Management
Thermal management of 5G devices and antennas is likely to become an increasingly hot topic as there is an exponential increase in heat generated in contrast to LTEs predecessors such as 4G.
The heat dissipation of smart devices will affect their maximum receiving rate. This means that, no matter how good your network connection is, the device's ability to properly manage heat will reduce its data handling performance. This is a significant challenge for edge devices such as 5G-enabled phones that are packed with more antennas and components. New innovations in component technology, and new systems to regulate and redirect heat or operation will be required to ensure maximum receiving rate.
Identifying thermal issues
There are several techniques to identify potential thermal issues. Small-size thermistors strategically placed on your circuit board can sense where thermal activity is occuring. Thermistors sense temperature and can provide feedback to various parts of the circuit when thermal issues arise.
Reducing heat
5G’s antennas, and the devices that drive them, generate more heat than their LTE predecessors. This creates new cooling problems for wireless devices and systems.
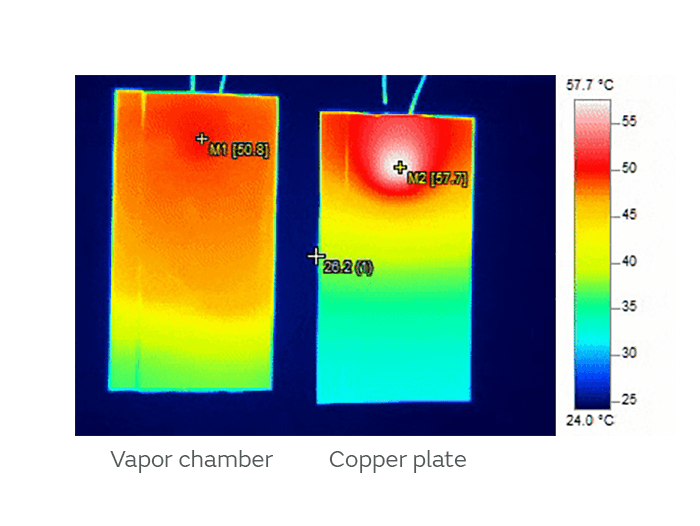
Utilising copper plates helps with heat dissipation, dispersing heat down towards the bottom of the PCB. Whilst this helps, as you can see in the below example, there are still hots spots. New innovations, such as ultra-thin vapor chambers, can alleviate this issue. This technology works by sandwiching two copper plates between a liquid cavity, as the liquid heats up it turns to vapor, dissipating the heat faster and more effectively.

Watch our onDemand webinar:
5G: Managing componet-level risks to commercial success
Duration: 45 min + Q&A