5G: Technology
5G Mission Critical Systems
Due to the ultra-high-reliability and low-latency communications (URLLC) of 5G, Mission Critical Communications (MCC) has been highlighted as a key area as part of the 3GPP Release. Delivered as part of a core network service it will allow emergency services to replace traditional radio, with more modern communications methods already available to smart phone users.
Mission-critical systems require real-time functionality with the lowest possible delay in the network. Reliability creates confidence in users that they can depend on communications, even in life-threatening situations.
With 5G, mission critical networks will evolve beyond traditional Push-to-Talk to include Push-to-Video, video sharing, group chat, file sharing, location sharing and much more – all with the proper prioritization of mission critical scenarios.
This technology evolution is also enabling a wider range of applications and use cases to deliver efficient, safer and cost-effective solutions via commercial mobile networks that are embedded with specialized mission-critical capabilities.
5G, when combined with Multi-Access Edge Computing (MEC), will help bring content and applications closer to the network edge, providing more efficient, reliable and cost-efficient services. Instead of sending all data to a cloud for processing, the network edge will be able to analyse processes and store the data. Collecting and processing data closer to the customer reduces latency and brings real-time performance to high-bandwidth applications.
5G IoT Intelligent Mobility (V2X, C2X)
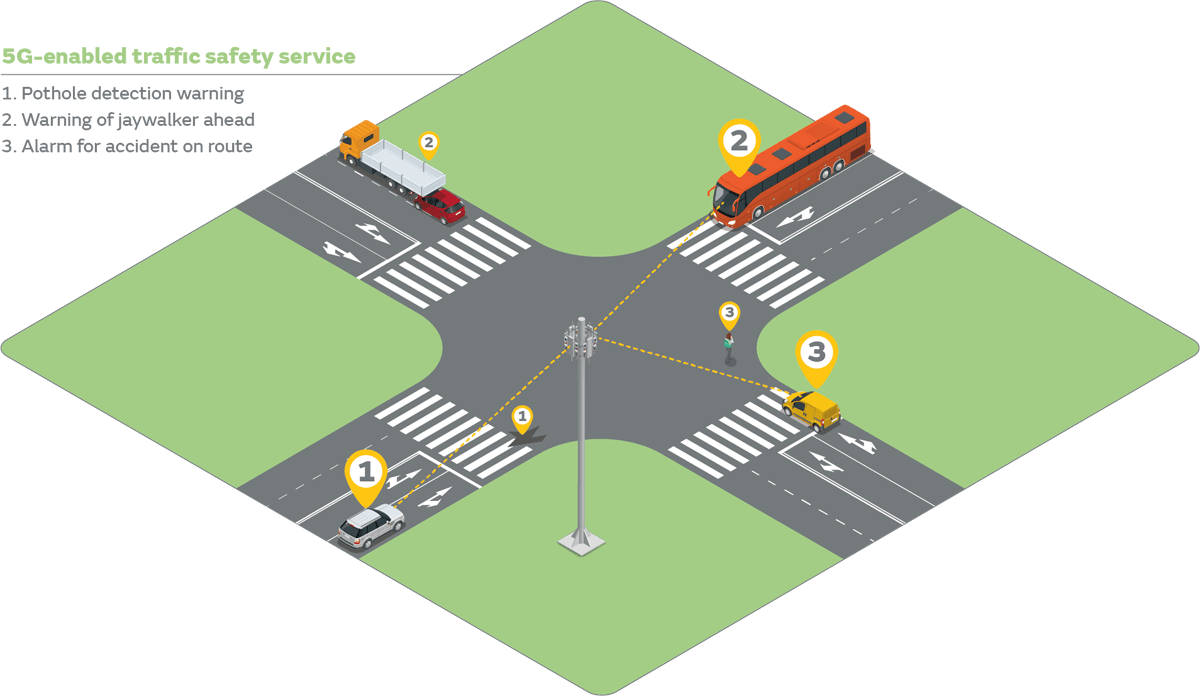
In the short term a key area for Automotive 5G will be the sharing of real-time communication, providing interconnected data on traffic and road conditions. 5G-based V2X will be introduced as part of 3GPP Rel-16 this year and is likely to provide many benefits to users, as well as improving road safety.
In Vehicle entertainment
5G will bring improved driver and passenger experience with streamlined delivery of information such as data intensive video or music streaming. Current applications will be enhanced to include in-car retail, AR/VR navigation, enhanced driver feedback and a host of other sophisticated in-vehicle applications.
5G: Video Surveillance
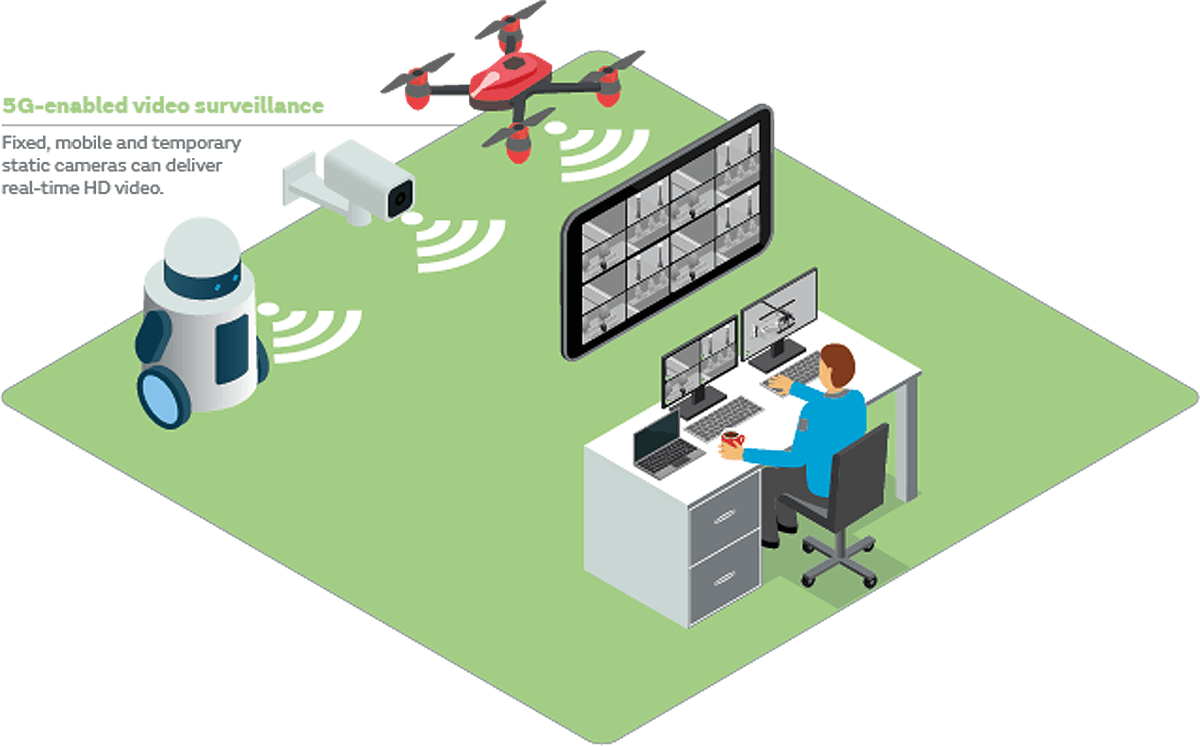
Due to the rise in terrorism, governments and cities continue to invest in surveillance and security systems. Whilst most video security networks rely on wired networks, wireless networks are increasingly adopted as a cheaper and more efficient option. Cellular connectivity, in particular LTE, is now a popular option for temporary static installations such as at public events like concerts and festivals as well as for mobile video such as in police cars, public transport, surveillance drones or body-worn equipment used by law officers. 5G will improve the performance for remote access to live and recorded HD video, the adoption of 5G will provide more sophisticated video content analytics in real-time, and the deployment of massive numbers of cameras.
5G: Medical and healthcare
The Internet of Healthcare Things (IoHT) has become increasingly more important in the midst of the COVID-19 pandemic. 5G is expected to support a number of use-cases to support patient care and hospital management. These include wearable devices, secure online consultations and remote procedures like robotic surgery. These options will greatly improve resource efficiency to improve patient care.

Watch our onDemand webinar:
5G: Managing componet-level risks to commercial success
Duration: 45 min + Q&A


