Noise suppression technologies/case study introduction (Automotive)
For automotive LANs Suppression of noise in CANs using common mode choke coils (2) Radiated noise evaluation
■Evaluation system
| Measurement frequencies : | 150 kHz to 1 GHz |
|---|---|
| Test standard : | CISPR25 Ed.3 (150 kHz to 1 GHz) |
| DUT : | CAN transceiver (made by company A) |
| Evaluation items : | Common mode choke coils (DLW43SH510XK2) |
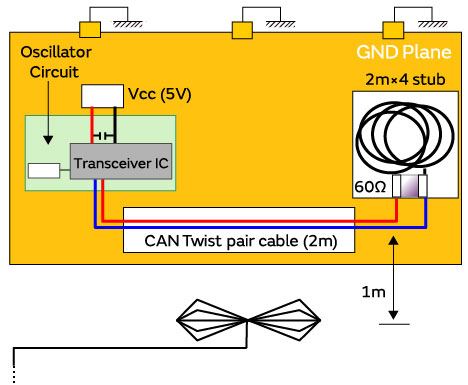
Radiated noise evaluation / Table of equipment used
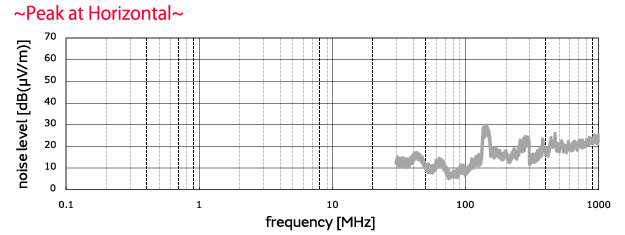
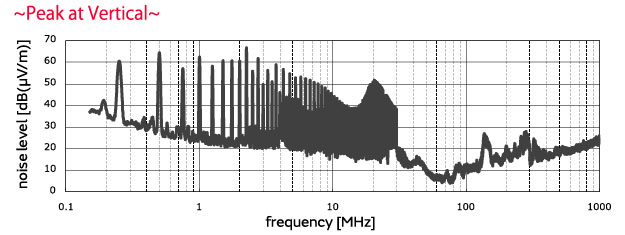
■Evaluation results No filter used, 250 kHz pulses
■Evaluation results DLW43SH510XK2 used, 250 kHz pulses
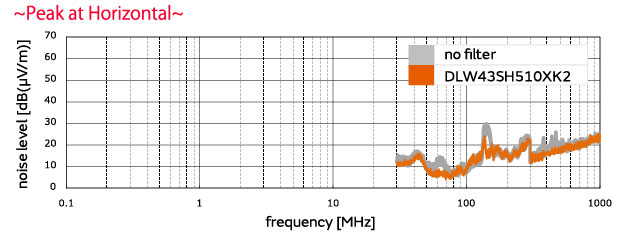
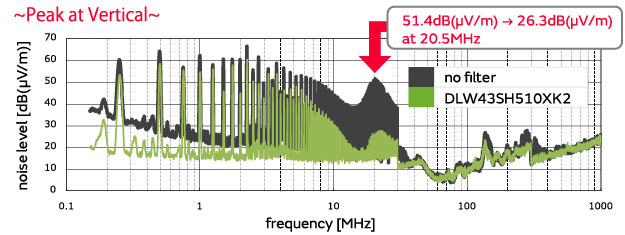
A noise-suppression effect was achieved by adding the DLW43SH510XK2.
(Noise was reduced by 25.1 dB at a 20.5 MHz vertical polarized wave frequency.)
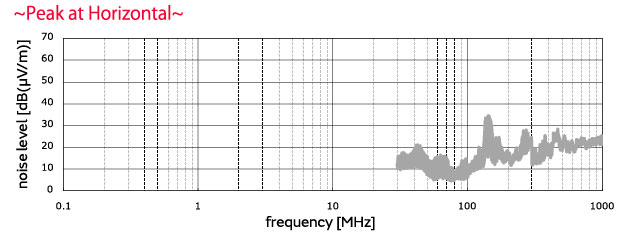
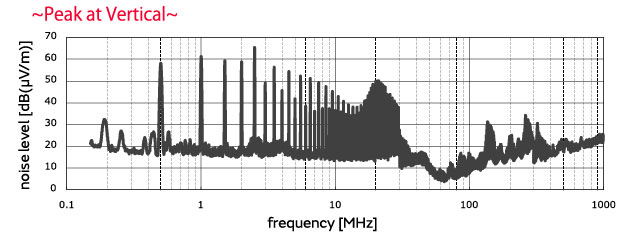
■Evaluation results No filter used, 500 kHz pulses
■Evaluation results DLW43SH510XK2 used, 500 kHz pulses
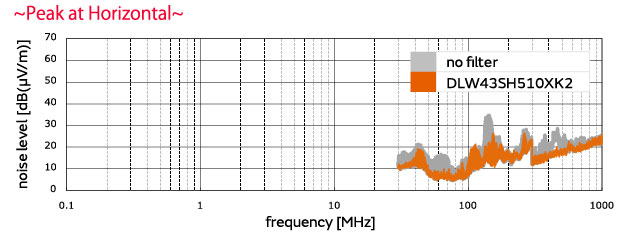
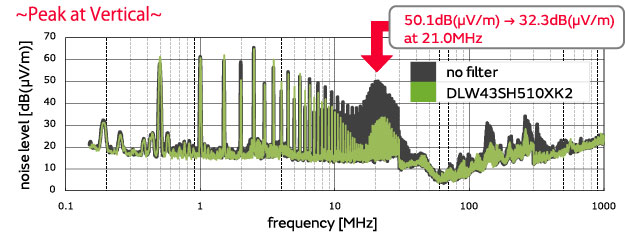
By adding the DLW43SH510XK2, a noise-suppression effect was achieved.
(Noise was reduced by 17.8 dB at a 21.0 MHz vertical polarized wave frequency.)
Summary of radiated noise evaluation effects
■250 kHz pulses
When no filter was used, a high level of noise was found from 150 kHz to 30 MHz.
By adding choke coil DLW43SH series, a noise-suppression effect was achieved.
The DLW43SH series achieved a noise-suppression effect of approx. 26 dB at a 20.5 MHz vertical polarized wave frequency.
■500 kHz pulses
When no filter was used, a high level of noise was found from 150 kHz to 30 MHz.
By adding choke coil DLW43SH series, a noise-suppression effect was achieved.
A noise-suppression effect of approx. 18 dB at a 21.0 MHz vertical polarized wave frequency was achieved.
- Continue reading:BCI tests
