Noise suppression technologies/case study introduction (Automotive)
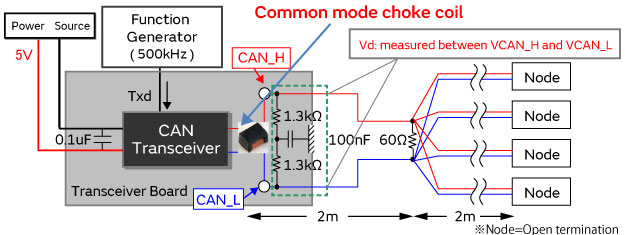
For automotive LANs Suppression of noise in CANs using common mode choke coils (6) Waveform evaluation
Measurement conditions
The star topology shown below was used to conduct the waveform evaluation. On the CAN evaluation board, 500 kHz pulses were input from the function generator to the Txd terminal of the transceiver made by company A to generate the CAN signals. Open terminations were used for the nodes at the reception to simulate high-impedance ICs.
As the waveforms, differential voltage Vd between CAN_H and CAN_L after transit through the filter was measured.
Evaluation results
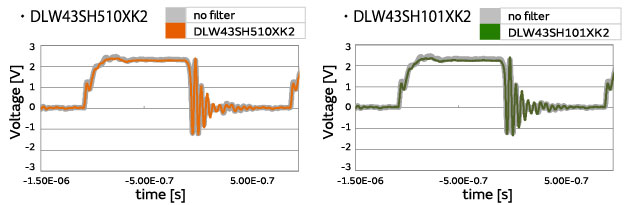
Summary of waveform evaluation results
Compared with when no filter was used, hardly any effect on the waveforms was found with the DLW43SH series.
Summary
Radiated noise evaluations using a CAN evaluation board as well as BCI tests and waveform evaluation were carried out.
<Evaluation results>
Radiated noise evaluation
By adding the DLW43SH series, it was verified that a noise-suppression effect was achieved.
For 250 kHz pulses, the noise-suppression effect is approx. 25 dB at a 20.5 MHz vertical polarized wave frequency.
For 500 kHz pulses, it is approx. 18 dB at a 21.0 MHz vertical polarized wave frequency.)
BCI tests
With the DLW43SH series, malfunctioning was suppressed, and 100 mA was cleared at all frequencies (1 MHz to 400 MHz).
Waveform evaluation
With the DLW43SH series, hardly any effect on the waveforms was found compared with cases of short-circuiting.
