Batteries


The lithium-ion batteries changing our lives
This five-part series introduces the various possibilities and future promise of lithium-ion batteries. In the final installment, we look at the reasons why lithium-ion batteries are said to be "batteries that contribute to the realization of a sustainable society" and examine environmental load reduction, recycling, SDGs, and other perspectives to explain the kinds of roles played by lithium-ion batteries in a sustainable society under the supervision of Ryoji Kanno, Professor Emeritus at the Tokyo Institute of Technology.

Supervisor: Ryoji Kanno
Institute Professor (Professor Emeritus), Institute of Innovative Research, Tokyo Institute of Technology
In 1980, he completed his master’s degree in inorganic and physical chemistry at the Graduate School of Science, Osaka University. In 1985, he became a Doctor of Science. After working as an associate professor in the Faculty of Science at Kobe University, he became a professor at the Tokyo Institute of Technology Interdisciplinary Graduate School of Science and Engineering in 2001. In 2016, he became a professor at the Tokyo Institute of Technology School of Materials and Chemical Technology. In 2018, he became a professor at the Tokyo Institute of Technology Institute of Innovative Research and a leader in the All-Solid-State Battery Unit. In 2021, he became an Institute Professor at the Tokyo Institute of Technology Institute of Innovative Research and director of the Research Center for All-Solid-State Battery.
INDEX
1. Low-environmental-impact lithium-ion batteries
2. Advantages of replacing lead-acid batteries with lithium-ion batteries
3. Can lithium-ion batteries be recycled?
4. Lithium-ion batteries contributing to the creation of a sustainable society

Why are lithium-ion batteries said to “contribute to the realization of a sustainable society?” One reason is that the use of lithium-ion batteries in various applications spreads electrification, reducing the use of fossil energies such as oil and gas, which is thought to lead to the curbing of global warming.
Lithium-ion batteries are also said to have a low environmental impact because they do not use substances such as cadmium, lead, and mercury as materials. Substances like cadmium, lead, and mercury have always existed in nature, so they do not have a major impact on the natural environment itself. However, it is said that their excessive consumption can cause harm to living creatures. In that regard, the main substances used as lithium-ion battery materials—lithium, carbon, manganese, nickel, cobalt, etc.—are said to have relatively low environmental impact.
Lead-acid batteries are often compared to lithium-ion batteries. Batteries are divided roughly into three types depending on the type of energy that generates the electricity: chemical batteries, physical batteries, and biological batteries. Chemical batteries are batteries that generate electricity by internal chemical reactions to extract their electrical energy. They are classified into three types: disposable primary batteries such as dry cell batteries, secondary batteries that can be recharged and used repeatedly, and fuel cells that continuously extract electricity generated by chemical reactions. Lithium-ion batteries are often compared to lead-acid batteries; both are classified as secondary batteries of the chemical battery type.
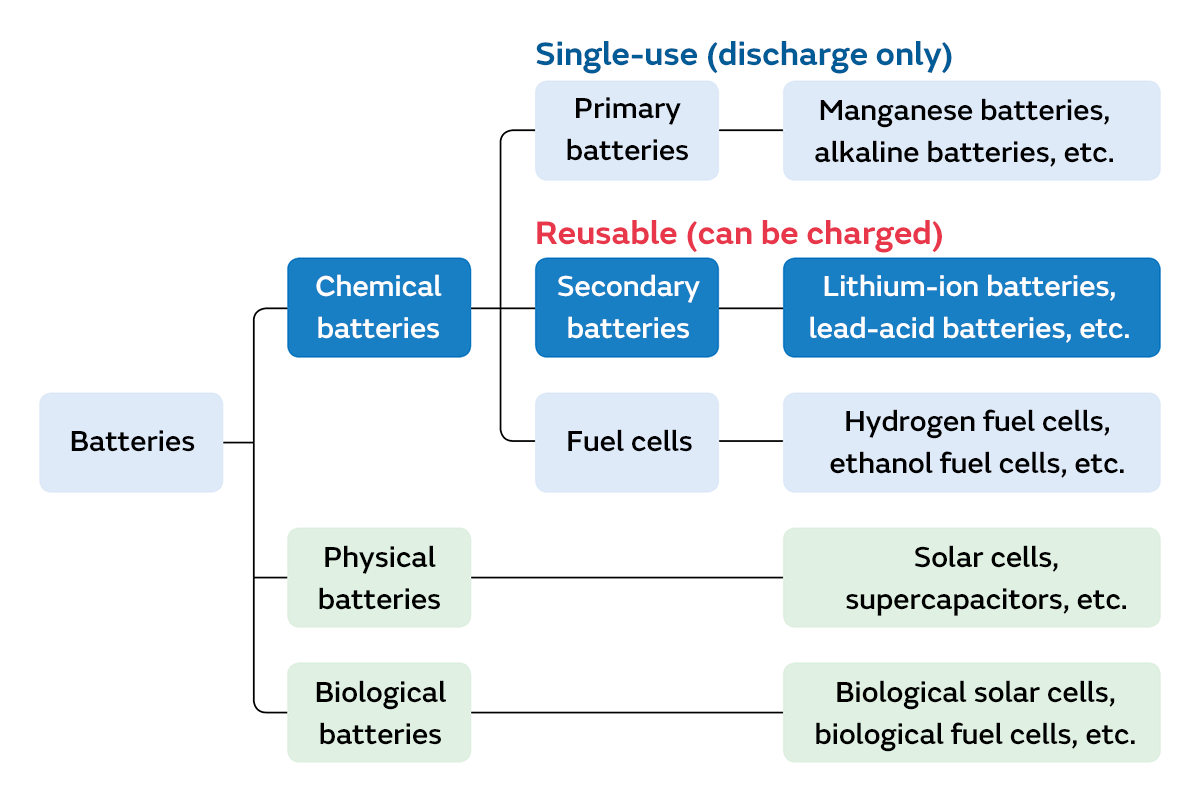
Among secondary batteries, lithium-ion batteries are thought to have a lower environmental impact than lead-acid batteries in terms of the materials used. However, since lead is a substance that is easy to obtain worldwide, lead-acid batteries are cheaper than lithium-ion batteries. Lead-acid batteries are also highly reliable batteries based on technology that is pretty much completely established at this point. Because they have other advantages such as these, lead-acid batteries are used in many fields and applications, including automobile batteries.
However, the use of lithium-ion batteries will increase more and more in the future. It is thought that even where lead-acid batteries are currently used, they will gradually be replaced by lithium-ion batteries. Some advantages of using lithium-ion batteries instead of lead-acid batteries are given below.
Excessive consumption of substances such as lead can harm living creatures, but substances such as lithium, carbon, manganese, nickel, and cobalt—the main materials in lithium-ion batteries—are said to have a low environmental impact. Therefore, it can be said that lithium-ion batteries have an environmental advantage over lead-acid batteries.
Lithium-ion batteries have higher energy density and are more powerful than lead-acid batteries. Energy density is a number that represents the amount of energy that can be extracted per mass or volume; the higher the value, the higher the performance of the battery. Comparing energy density per unit weight (volume), lead acid batteries are about 25–50 W⋅h/kg (50-100 W⋅ h/L) and lithium-ion batteries are about 100–250 W⋅h/kg (200–700 W⋅h/L).
In addition, chemical batteries have a phenomenon called “self-discharge,” whereby electricity decreases because the chemical reaction occurs little by little inside even when the battery is not in use. However, since lithium-ion batteries do not self-discharge, the batteries do not easily deteriorate, and they last longer as a result.
In Japan, in some cases, batteries that still have capacity are reused for different applications and in other cases, useful resources are taken out from batteries that are completely unusable and recycled at a factory.
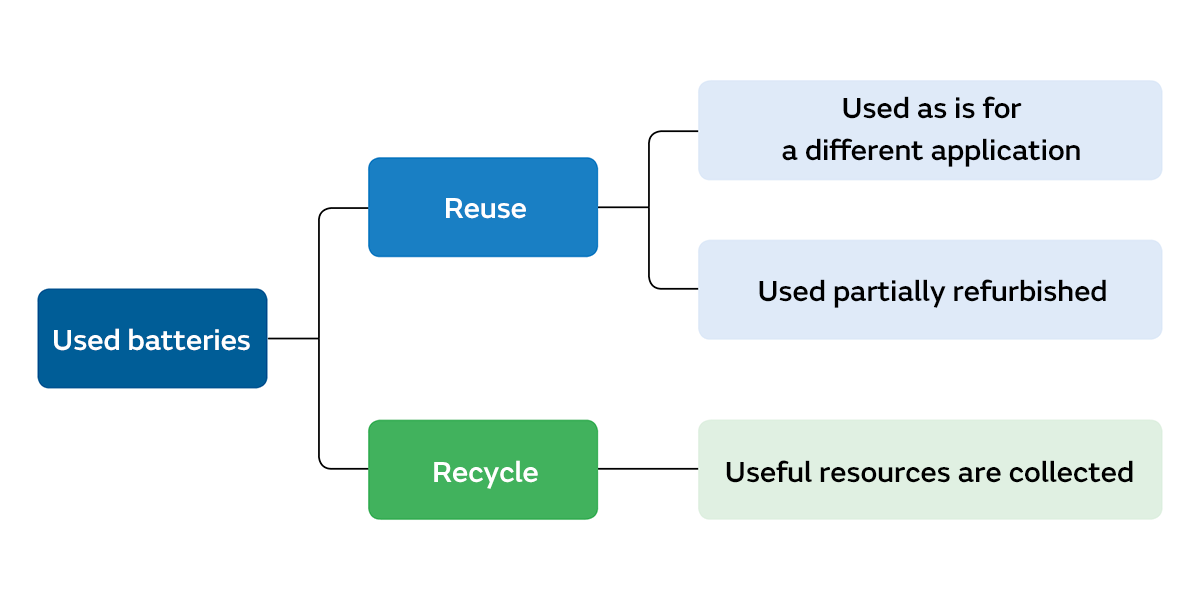
In the case of electric vehicles, when the distance that can be traveled on a single charge becomes shorter, it is judged that the battery has deteriorated. However, since the lithium-ion batteries for vehicles are large and have high capacity, even if they cannot be used anymore in cars, there is still a considerable amount of capacity. So, it is possible to reuse these batteries for other purposes, either as they are or by replacing or repairing some part of them.
Although the recycling process for lead-acid batteries is established, the recycling of lithium-ion batteries is still in the process of development. Generally, when extracting useful resources from used batteries at a factory, materials such as metal and plastic are sorted in a preliminary procedure and then the raw materials of the cathode are separated. Lithium-ion batteries use lithium and cobalt, both rare metals, as cathode materials. So, if recycling technology were established, they could be used effectively. However, with current technology, the challenge is that the cost of recycling is still high.

In contemporary society, fossil fuels such as oil, coal, and natural gas play a major role as energy sources. However, fossil fuels come with problems such as resource depletion and carbon dioxide emissions. In order to move toward a sustainable society in the future, it is important to break away from fossil fuels. One solution attracting attention is electrification. If more things use electricity as a power source, the burning of fossil fuels to produce energy may decrease.
For example, taking lithium-ion batteries as the energy source for electric vehicles, they have a smaller environmental impact than driving while emitting exhaust gas from the burning of fossil fuels.
The concept of the smart city is also advancing to reduce environmental impact by utilizing lithium-ion batteries. For example, Kashiwa-no-ha Smart City in Kashiwa City, Chiba Prefecture, has built a distributed power supply network using technologies such as solar power generation and lithium-ion batteries, contributing to the effective use of electricity throughout the city. In addition, various experiments are being conducted at the community level in many parts of Japan regarding the creation of a sustainable society using lithium-ion batteries.
On the other hand, it cannot simply be said that “electrification equals environmentally friendly.” Even in the case of electrification, fossil fuels may continue to be used in the process of producing electricity. So, it is important to advance the introduction and expansion of renewable energy in parallel with electrification. Also, the solvent NMP, about which there are concerns regarding its impact on the environment and human health, is used in part of the manufacturing process for lithium-ion batteries. Efforts are already being made to reuse the solvent and remove it in an environmentally friendly manner, but further efforts are required, such as reducing the amount used and switching to alternative solvents.
Lithium-ion batteries have been studied since the 1970s, and they can now be used stably. Nevertheless, performance enhancements are still being pursued through research into new materials and other areas. What kind of future can we expect as the use of lithium-ion batteries expands going forward?
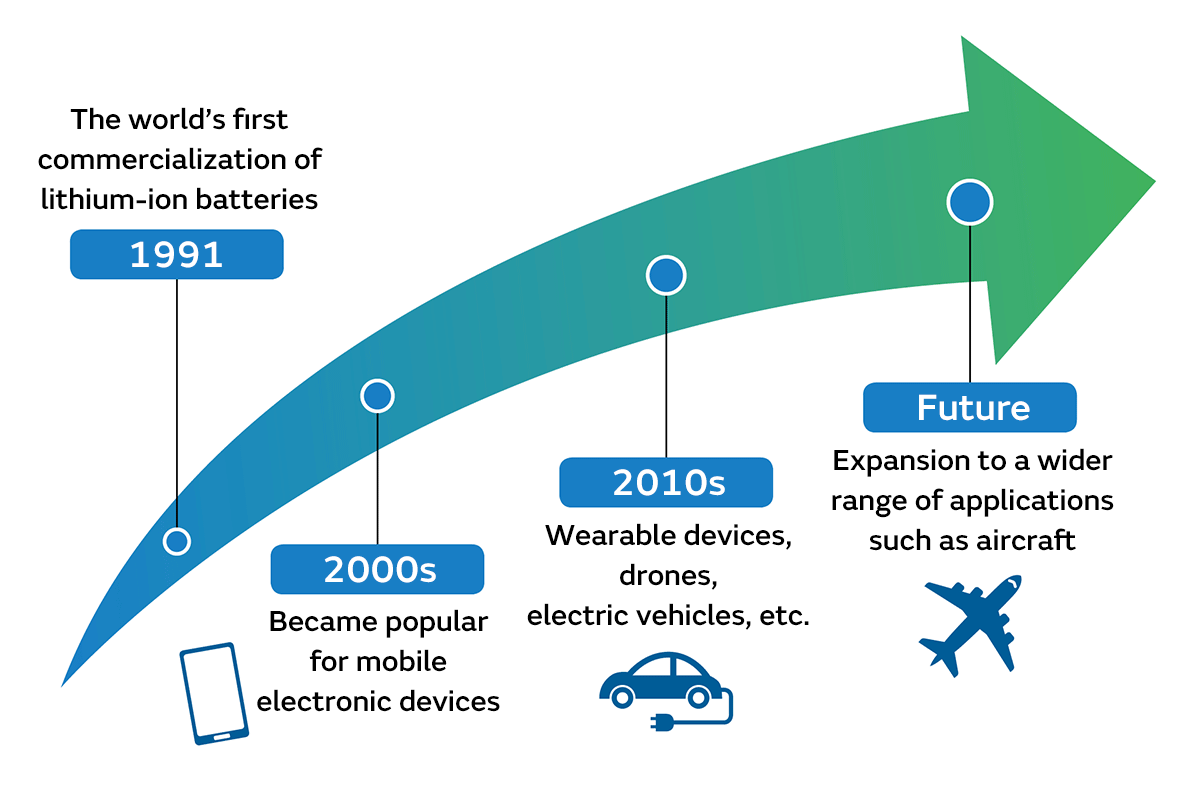
In the past, performance enhancements in lithium-ion batteries brought about the creation of various devices. In 1991, the world’s first lithium-ion battery was commercialized, and a mobile phone equipped with it was released. After that, they were put to use in a wide range of applications including video cameras, smartphones, drones, and electric vehicles. It can be said that the existence of lithium-ion batteries is why PCs and smartphones became more convenient and easier to use, becoming as ubiquitous as they are today.
In the future, if the performance of lithium-ion batteries improves even more, the spread of electric vehicles may advance further, and new means of transportation such as electric aircraft may come into practical use. Moreover, the use of lithium-ion batteries is already progressing in the medical field. For example, if various medical devices used in surgery were battery-powered, they would be easier to carry around. It may also become possible to perform emergency surgery immediately at the scene of accidents.
The possibilities of lithium-ion batteries are endless. Surely it can be said that they are a tool that not only makes our lives convenient, but also has such an impact as to change the structure of society.