LPWA Products LoRa (LoRaWAN) Modules


INDEX - LoRaWAN (Non-cellular LPWA) Primer – From Fundamentals to IoT Application Examples (1)
1. What is LoRaWAN?
2. LoRaWAN Communication Protocol Stack – Roles of LoRa and LoRaWAN –
3. LoRaWAN Network Construction – Configuration of the LPWA Devices, Gateway, Servers, etc. –
Column – What Is the Communication Protocol Stack?
INDEX - LoRaWAN (Non-cellular LPWA) Primer – From Fundamentals to IoT Application Examples (2)
4. Examples of IoT Solutions Utilizing LoRaWAN
4.1 Disaster Prevention System Using LoRaWAN and Environmental Monitoring Sensors
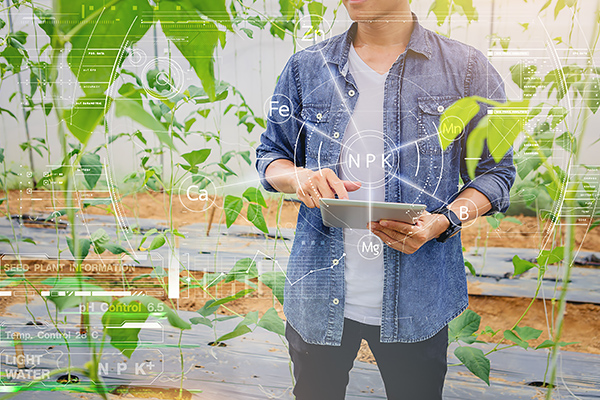
4.2 Smart Agriculture Using LoRaWAN and Soil Sensors
4.3 Community Infrastructure Smart Meters Using LoRaWAN
4.4 Adding Intelligence to a Solar Power Plant Using LoRaWAN
5. LoRaWAN Modules From Murata Manufacturing
5.1 Features of the LoRaWAN Modules From Murata Manufacturing
In the LoRaWAN (Non-cellular LPWA) Primer – From Fundamentals to IoT Application Examples (1), we introduced everything from basic knowledge including an overview of LoRaWAN and how it works to an example of network construction.
In the following section, we introduce examples in which a LoRaWAN network is actually used as an IoT solution and the LoRaWAN non-cellular LPWA modules that affect the size, performance, ease of use, and reliability of end devices.
LPWA wireless communication using LoRaWAN is used in a broad range of applications as a wireless communication network suited to various IoT solutions. Here, we show a few successful examples of applications utilizing LoRaWAN modules (Type ABZ).

To prepare for flood damage due to heavy rainfall, environmental monitoring sensors with superior durability were equipped with LoRaWAN and installed around rivers. This is an application that measures the amount of rainfall at various sites along the river with multiple LoRaWAN devices to gather data with long-range wireless communication and display the conditions on a terminal screen map. This makes it possible to verify heavy rainfall conditions from a smartphone, etc. and is helpful for preventing damage due to heavy rainfall and flooding.
At the same time, because the LoRaWAN modules have low power consumption and a long battery lifetime, the effort and cost required to change the device batteries and perform other maintenance can be kept to a minimum even if many sensors are placed outdoors.

In recent years, the demand for smart agriculture utilizing soil sensors and wireless communications has been increasing. Wireless operation is highly efficient for sensing soil conditions across a wide area or from a remote location. Therefore, the introduction of LPWA is attracting attention, because it has low power consumption, significantly reduces the frequency of battery replacement, and enables long-range wireless communication.
When conducting central management on an agricultural site or using it on farmland that is far from urban areas and settlements including mountainous areas, the non-cellular LPWA-based LoRaWAN is an effective solution because it can be used without considering contracts with carriers or whether the area is covered by the carrier base stations.
Furthermore, because Murata's soil sensors (able to simultaneously measure the EC [electric conductivity], Moisture [volumetric water content], and Temperature in the soil or water) and LoRaWAN modules are compact and able to withstand harsh environments, they enable stable applications that can be used outdoors.
For details about Murata's soil sensors, see the link below.
Soil sensor|Murata Manufacturing (murata.com)
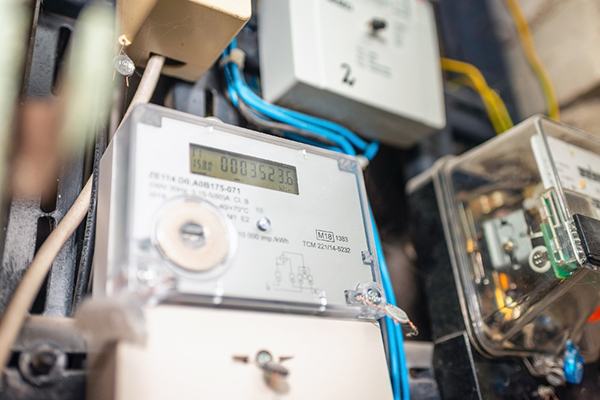

In the past, meter readers had to go on-site to check community infrastructure such as water, electricity, and gas. There have been an increasing number of successful examples in recent years where LoRaWAN modules were equipped in a large number of meters installed in an area to reduce the effort and cost of meter reading by gathering the usage data through LoRaWAN.
Moreover, this also makes it possible to detect excessive usage over a long period of time or suspension to send out alerts or remotely control the shutoff and restarting of supply services. In addition, because LoRaWAN is non-cellular LPWA, it can be introduced and operated without being tied to a carrier's service area.
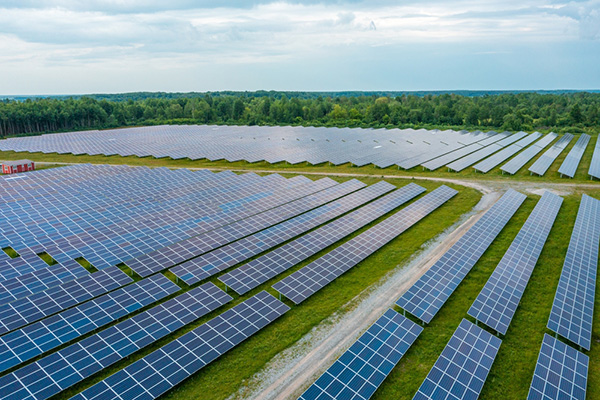

LoRaWAN can also be used in the renewable energy field. Because the panels for solar power generation placed across a large site are each connected to electrical transmission cables and other equipment, systems become complex when using long wired cables for data communication, which is essential to IoT, and the number of inspection points also increases. Utilizing the low power consumption and long-range communication of LoRaWAN to achieve wireless data communication for sensing and panel control enables simple, rational, and low-cost operation. Moreover, because the LoRaWAN modules have low power consumption and a long battery lifetime, they dramatically decrease the frequency of battery replacement and other forms of maintenance.
Murata Manufacturing produces compact and high-quality non-cellular LPWA (LoRaWAN) and cellular LPWA (LTE-M/NB-IoT) modules. The following section introduces the features and lineup of the LoRaWAN modules from Murata.
The LoRaWAN modules, which Murata Manufacturing provides to a diverse range of fields and applications all over the world, offer the following features.
At Murata Manufacturing, we offer a lineup of LoRaWAN-compliant LPWA modules that are widely supported for their superior specifications that balance communication speed and distance among the many non-cellular LPWA standards.

Non-cellular LPWA modules that are compliant with the LoRaWAN™ standard, which does not require a license. These modules also support the services offered by vendors in many regions around the world based on the radio laws of each country and region.
Type ABZ (CMWX1ZZABZ)|LPWA Products
A Type ABZ evaluation kit for verifying the operation and characteristics before introducing a large number of Type ABZ modules is available for purchase from STMicroelectronics.
In addition to the products described above, Murata plans to offer various LoRaWAN modules for sale with specifications and functions that meet the needs of the times and users going forward.
LoRa (LoRaWAN) Modules|Murata Manufacturing (murata.com)
INDEX - LoRaWAN (Non-cellular LPWA) Primer – From Fundamentals to IoT Application Examples (1)
1. What is LoRaWAN?
1.1 Comparison of LoRaWAN (Non-cellular LPWA) and Cellular LPWA
1.2 Primary LoRaWAN Applications
2. LoRaWAN Communication Protocol Stack – Roles of LoRa and LoRaWAN –
2.1 What is LoRa (Physical Layer)?
2.2 What is LoRaWAN (MAC Layer)?
3. LoRaWAN Network Construction – Configuration of the LPWA Devices, Gateway, Servers, etc. –
3.1 Example of Building Your Own LoRaWAN Network
3.2 Example of Building a LoRaWAN Network Using a Vendor
Column – What Is the Communication Protocol Stack?