Ceramic Capacitor NFM Series


Noise-control techniques are becoming increasingly important due to high-speed operation of ICs and electrification of automobiles.
This application note introduces examples of using the 3-terminal capacitor as a filter (feed-through connection) for radiated emission and conducted immunity.
For information on "through" and "non-through" connection, please click here.
Basics of Noise CountermeasuresLesson 11 Notes on the Use of Chip 3-Terminal Capacitors | Murata Manufacturing Articles (murata.com)
In the recent years, the switching frequency of DC/DC converters has increased due to the demand for miniaturization of circuits, and their harmonic noise tend to exist up to high frequencies.
In addition, the resonance due to parasitic inductance and floating capacitance of IC and PCB generates high level noise at high frequency.
As a countermeasure, this note introduces examples in which the 3-terminal capacitor is used at output line or input line of a DC/DC converter.
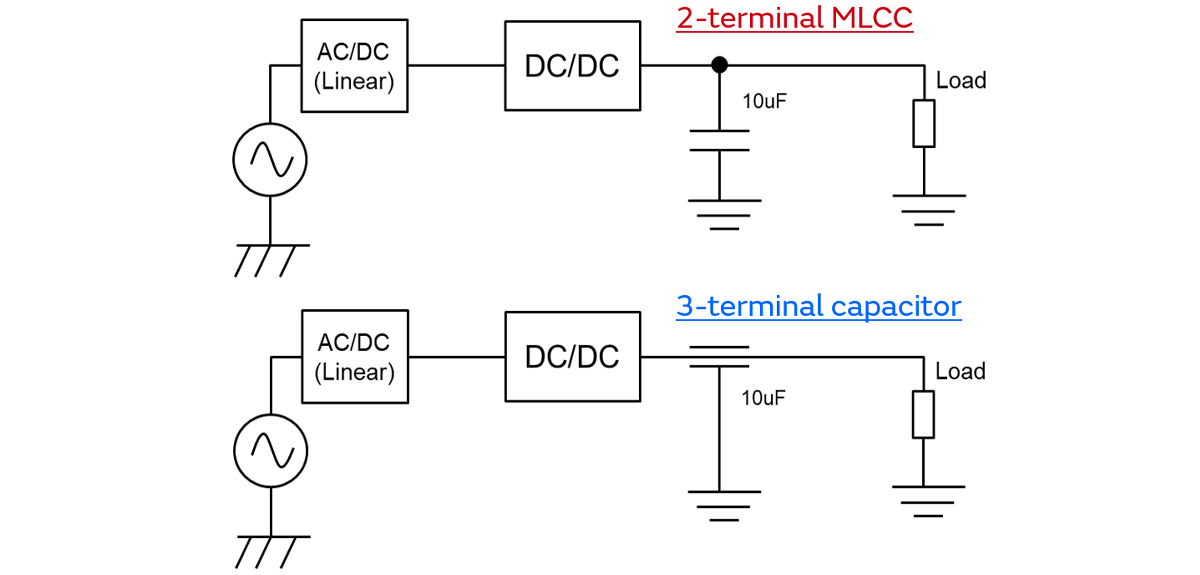
We compared noise reduction effect of a standard 2-terminal MLCC and a 3-terminal low-ESL capacitor.
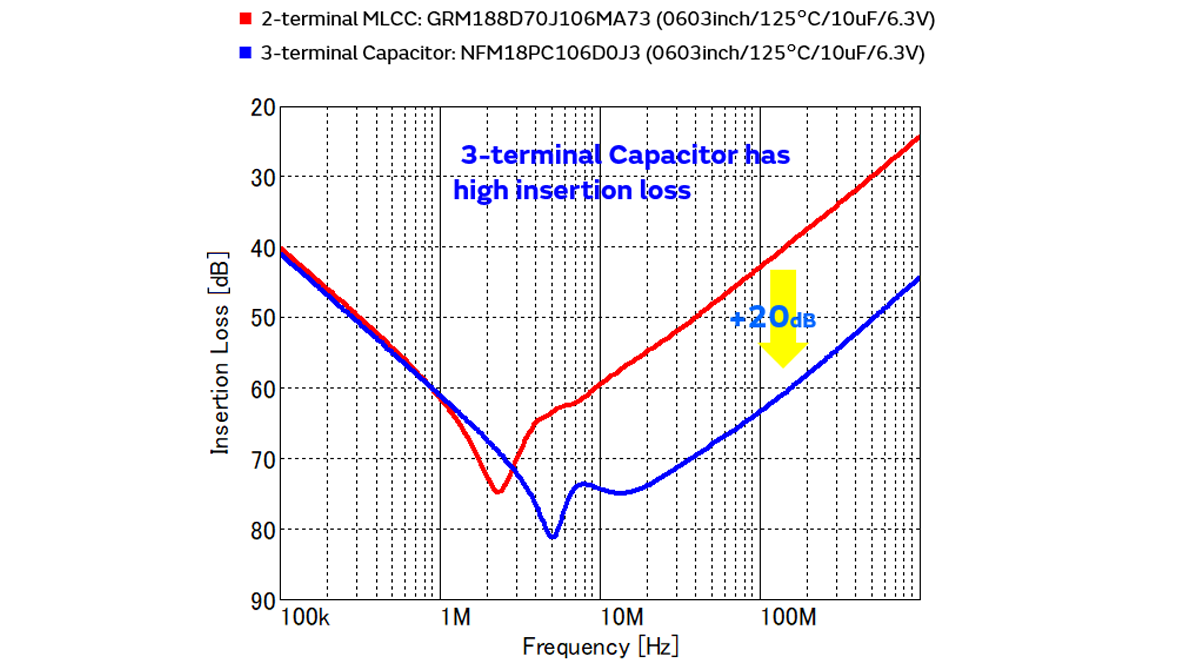
First, we show the frequency characteristics of the two insertion losses. It can be seen that the 3 terminal capacitor has an excellent filter effect of about 20dB in the region of 10 MHz or more.
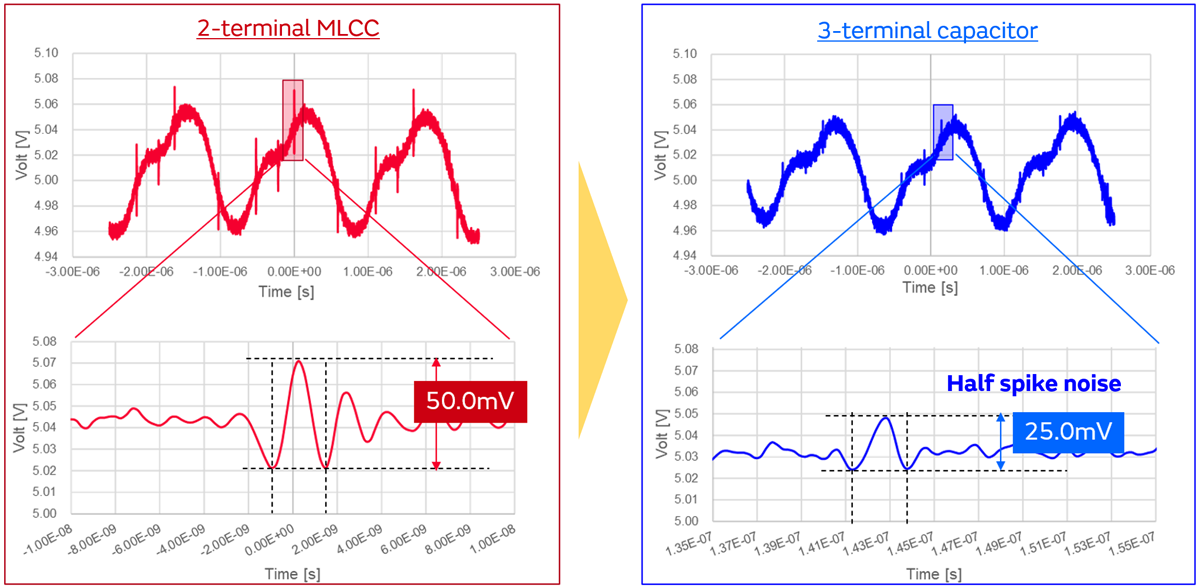
The DC/DC output voltage may have ripples and sharp spike noise as shown in the figure below.
Then, a 3-terminal capacitor instead of a 2-terminal MLCC can greatly reduce spike noise.
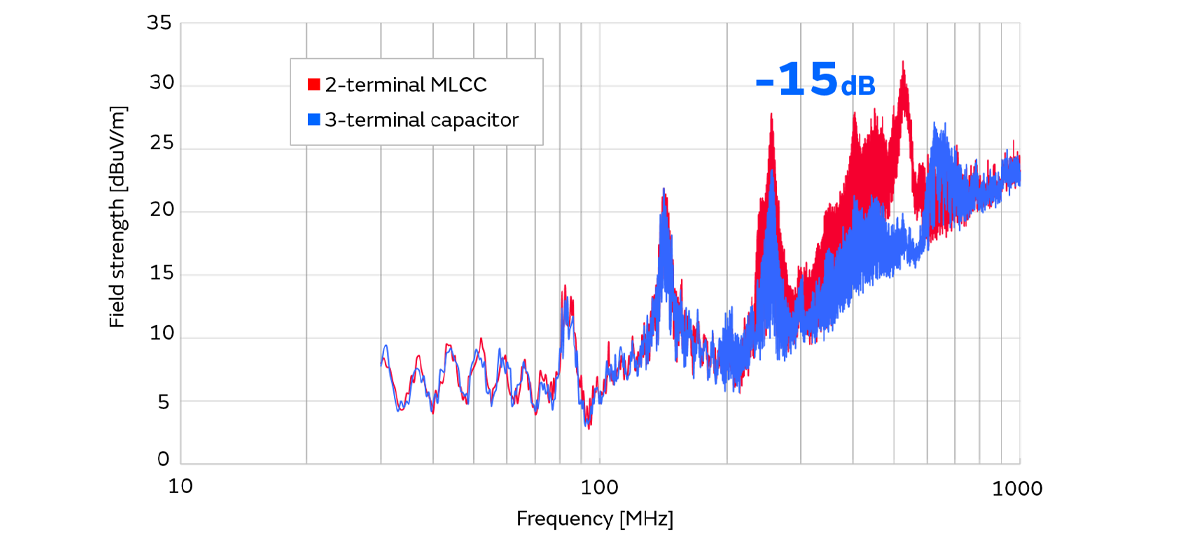
Next, the radiation noise measurement result (CISPR32/3m) is shown below.
By using the 3-terminal low-ESL capacitor, we were able to confirm that the noise reduction was more than 15dB compared with the 2-terminal MLCC.
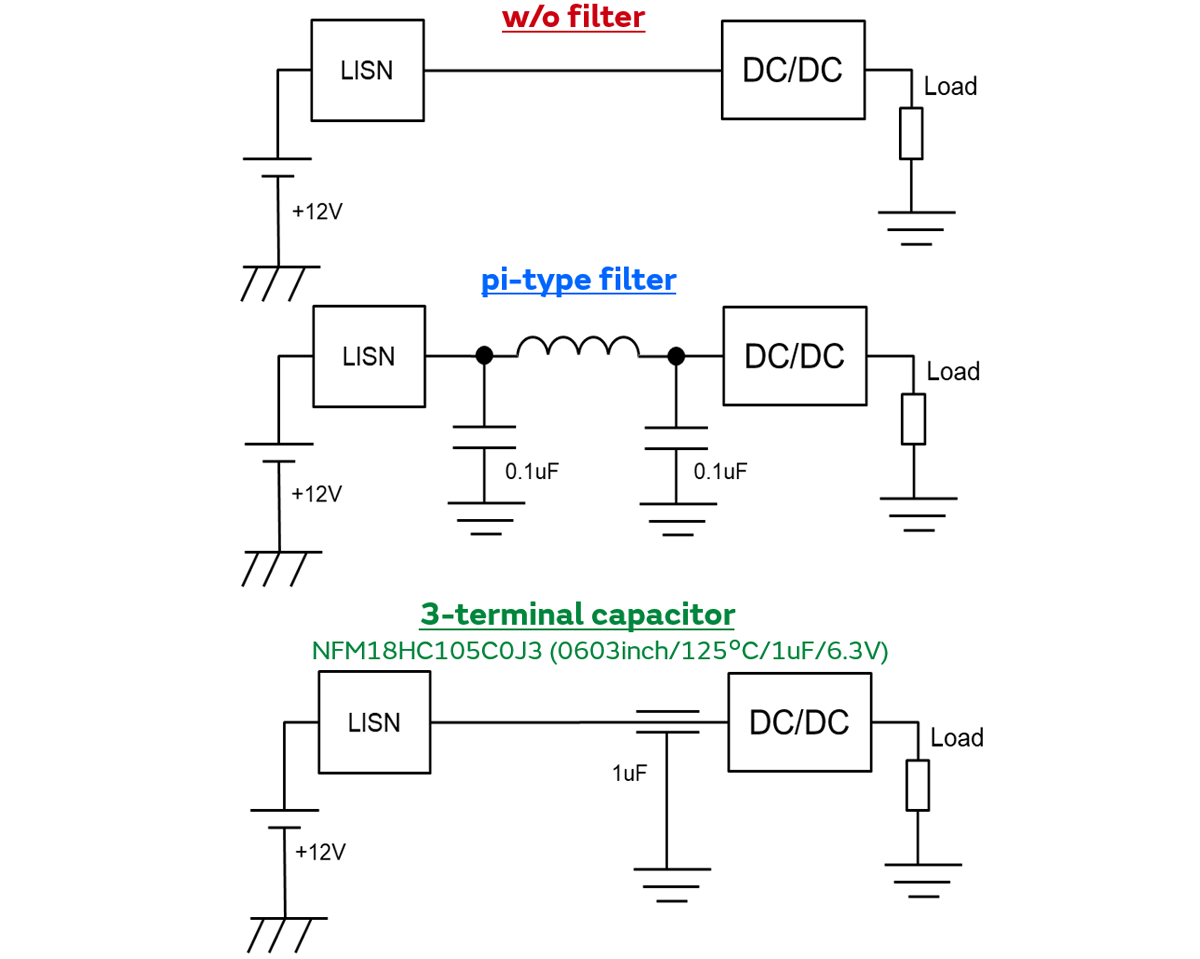
DC/DC converters generate large noise not only at output line but also at input line.
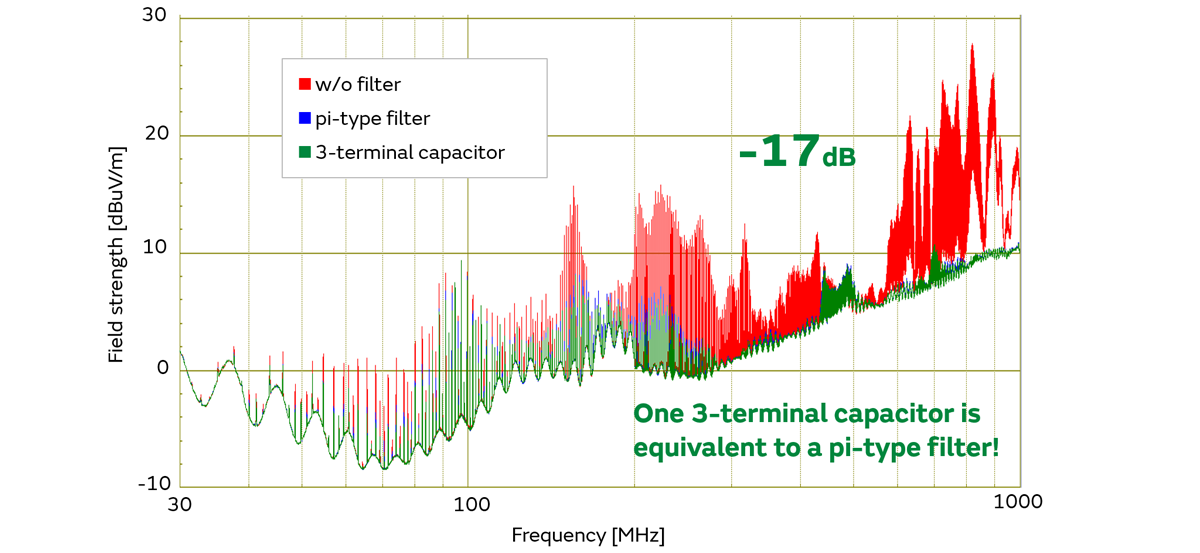
We arranged "No Filter", "pi-type filter" and "3-terminal capacitor" at the input power line of the DC/DC used in the on-board equipment, and compared the radiated emission noise of these 3 patterns.
As you can see the results, 1 element of a 3-terminal capacitor has the same noise reduction effect as a π-type filter (3 elements), which reduces the number of components.
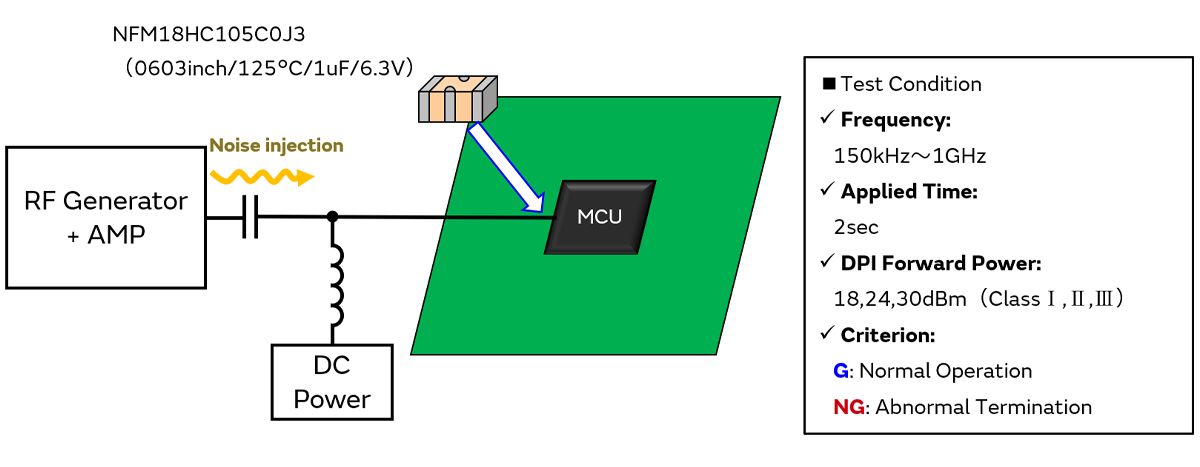
3-terminal capacitors can also be used for conducted immunity.
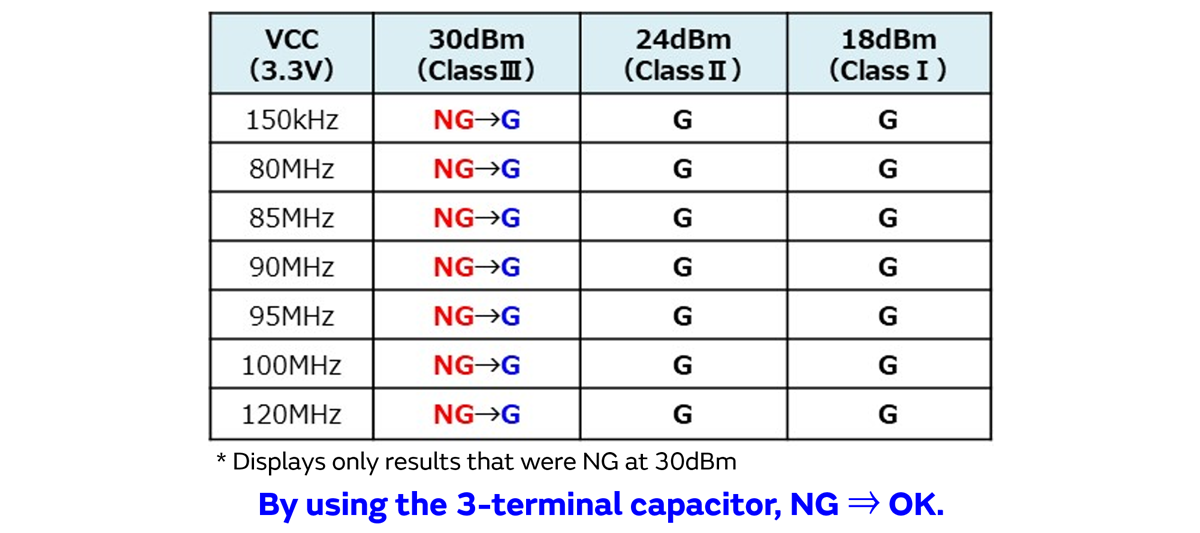
In the DPI test (IEC62132-4) which is the immunity evaluation test for semiconductors, we used the 3-terminal capacitor (through connection) at the MCU power line.
By using the 3-terminal capacitor, NG results improved to OK.
This article introduced the noise reduction effect of a 3-terminal capacitor (feed-through connection) featuring low ESL.
We presented the results of radiation emission and conduction immunity tests of DC/DC converters. In addition, it can be used to prevent conducted emissions and self-poisoning in electronic devices.
It can be used not only to add 3-terminal capacitors to electronic circuits, but also to replace 2-terminal MLCCs and filters currently in use.
Please consider using a 3-terminal capacitor as one of the solutions for noise control.