Capacitor
Capacitor Guide
In the electronics industry, lead-free products are being adopted and developed in great numbers. Conductive adhesives have gained attention as lead-free products (solder alternative products) that are better for the environment. They are currently being used in electronic parts, most notably the multilayer ceramic capacitor, as well as LED die-attach adhesives, CCD and other modules with low heat resistance, resin seal modules in which melting joints are problematic, vehicle-mounted modules that require high heat resistance and temperature-resistant cycle properties, etc.
If a conventional solder-mounted part is placed in an environment subjected to harsh temperature changes and it receives a thermal shock, the load on the solder part increases according to the difference between the expansion/contraction rates of the part and the substrate, causing cracks to form. However, conductive adhesive mounts rarely pose this risk. An example of a conductive adhesive mount is shown in photograph 1.

Conductive adhesives are anticipated to have wide-ranging applications in the future. Once conductive adhesives have been internationally standardized, they are expected to replace several of the conventional solder-mount markets.
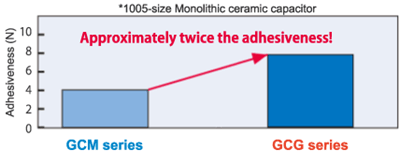
Our company has commoditized the multilayer ceramic capacitor GCG series for the above-mentioned markets. This series includes external electrodes consisting of Ag (silver) -Pd (palladium) and exhibits reliable adhesiveness with conductive adhesives. The GCG series is a structure for mounting electronic parts to be placed in harsh temperature environments, for example, engine control units for vehicles, various sensor circuits, etc. Figure 1 compares the structure of this series with that of the conventional external electrode plating (GCM series), and Figure 2 compares the adhesiveness of this series with that of the conventional product.
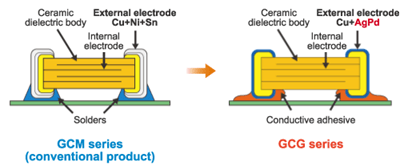
Conductive adhesives produce strong part adhesiveness by an energy-saving, low-temperature process. They are designed with an epoxy resin containing an Ag filler. Compared to this adhesive, the conventional Sn (tin) plating terminal electrode structure cannot guarantee adequate adhesiveness due to its smooth surface, and it is not very reliable, because differences in electric potential at Ag and Sn contact surfaces cause potential difference corrosion over time. To resolve both of those problems, our company created an external electrode that possesses an Ag structure. The surface has a convex and concave quality specific to thick-film-fired electrodes that ensures the area of contact with the adhesive. Also, this structure avoids potential difference corrosion by ensuring that the contact surfaces are both Ag surfaces. The addition of Pd makes it possible to prevent the Ag surfaces from oxidizing.
The conductive filler metal contained in the conductive adhesive and the Ag used in the external electrode carry the risk of insulation properties decreasing if a difference in electric potential occurs in an extremely high-humidity environment. This difference is caused by the electromigration phenomenon between positive and negative lands and between capacitor electrodes. Various strategies that reduce this risk, such as optimizing the metal alloy ratio between Ag and Pd, have resolved these problems in recent years.
Therefore, applications toward conductive adhesives for narrow pitch are certainly possible, as well as reliable long-term use in harsh environments, such as various electronic control circuits inside vehicle engine rooms. (However, depending on the environment in which the circuit is used or on the elapsed time, results other than those obtained in tests could occur. Therefore, in order to use this conductive adhesive more safely, it is recommended that you take precautionary measures such as sealing with moisture-resistant silicone, etc.)
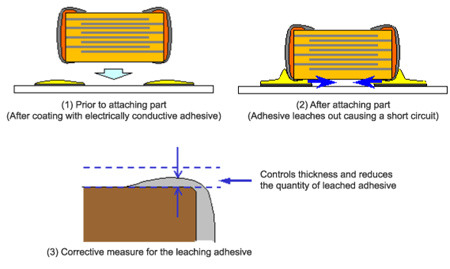
With the conductive adhesive mount, short circuits can occur between electrodes if adhesive leaches out at the lower surface of the part during mounting.
Figure 3 (1) and (2) show schematic diagrams of before and after mounting a part with a conductive adhesive mount. Depending on the shape of the external electrode, conductive adhesive could leach out between the electrodes, causing short circuits and other problems. To address this, adjustments, such as adjusting the quantity of adhesive, must be made and print patterns, etc. must be optimized. However, as shown in Figure 3(3), our capacitor was designed with a structure that controls the shape of the part, making it difficult for mounting problems to occur. This countermeasure also reduces adhesive leaching and allows for more reliable use.
By combining the broad-ranging temperature characteristics and rated voltage, which are the advantages of our multilayer capacitors, with the above-mentioned Ag external electrode technology, our company was able to create a similarly broad GCG series lineup. We offer sizes from a 1005 size (in mm) (GCG15 series) to a 3225 size (in mm) (GCG32 series) and provide the ability to select a volume from 10pF to 10μF. We also offer 150°C-compatible products (X8L/X8R/X8G characteristics) as well as 125°C-compatible products (X7R characteristics).
The GCG series lineup is shown in Table 1.
To meet the harsh heat-shock and mechanical-shock requirements of the automobile and other markets, we have commoditized not only products for conductive adhesives, which we introduced in this instance, but also products (GCJ series) that use resin electrodes for some of the external electrodes. For details, see below.
▼GCJ series
In the future, we will consider promoting additional mounting methods that are gentle to the environment, such as lead-free methods. As mounting methods change, our company will continue to proactively develop products that are optimal for those mounting methods.
* The content of this article, listed in the January 28, 2010 issue of "Hi-Technology," 2nd Part of Denpa Newspaper, was restructured.
* For more details on the GCG series, please refer to the following:
▼GCG series page
▼GCG series part number list
The information presented in this article was current as of the date of publication. Please note that it may differ from the latest information.