Edge AI Modules


The globalization of supply chains is being formed on production lines that are able to supply only the required quantity of products at the time required. This means that an obstacle arising in one place in the production line may strike a major blow to the entire supply chain.
The causes of production delays and stoppages include conflicts, disasters, raw material shortages, and equipment and device failures. In particular, production stoppages and the outflow of defective products due to equipment and device failures may lead to major problems for manufacturers. These problems include the expense required to recover those defective products and opportunity losses due to product supply stoppages. Therefore, equipment maintenance, which bears responsibility for the stable operation of the production line, is an important issue that holds the key to the life of manufacturers.
The importance of equipment maintenance has been strongly expressed up to now. The techniques of equipment maintenance have also been advancing from breakdown maintenance to preventive maintenance and then onto predictive maintenance as well in recent years.
We introduce in an easy-to-understand manner equipment maintenance that is continuing to evolve in this way—from basic knowledge such as the types of equipment maintenance and their advantages and disadvantages to the technologies to realize the predictive maintenance that is considered the ideal form of equipment maintenance.
Equipment maintenance refers to the activities to keep various production equipment in factories functioning normally. It is also called “machine maintenance.” The purposes of equipment maintenance are cited as being, for example, to prolong the life of machine components used in equipment, to shorten machine and device downtime, and to prevent unexpected failures in addition to repairing equipment that has failed.
Moreover, equipment maintenance up to now has mainly focused on machines and devices. Now, the focus is also on the software that controls the Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) and machines and devices with the conversion of regular factories into smart factories using industrial robots, machine vision, and other technologies.
There are other terms similar to maintenance such as “upkeep” and “care,” but these are the same as equipment maintenance. The reason is that they all involve inspecting equipment and then servicing or repairing it as necessary so that it does not fail.
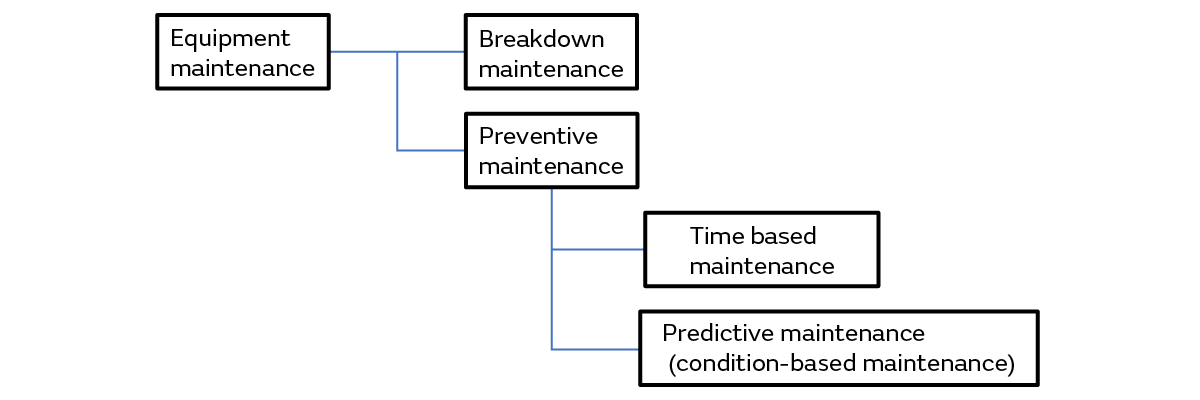
Equipment maintenance includes breakdown maintenance and preventive maintenance. Preventive maintenance is further broken down into time-based maintenance and condition-based maintenance (Figure 1). We explain here the features and the advantages and disadvantages of each type.
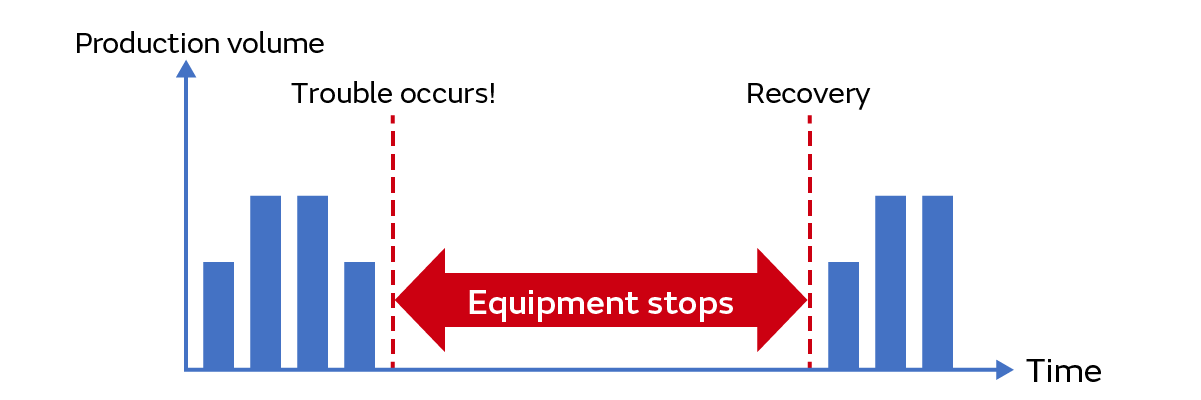
This is maintenance that is performed after a piece of equipment’s functions have declined or after it has stopped functioning (Fig. 2).
Advantages:
The advantages of breakdown maintenance include the fact that the burden on maintenance work is low because the condition of the equipment is not checked until it fails or a malfunction is discovered. Another advantage is that it keeps the costs involved in maintenance low in the case of minor failures.
Disadvantages:
Failures and malfunctions occur unexpectedly. Therefore, there may be delays in obtaining repair components, and so it may take some time to carry out repairs. In addition, there are risks such as major disruptions to production plans if the failure or malfunction occurs in a core piece of equipment. Furthermore, if there is a delay in discovering the failure or malfunction in the equipment, it may lead to defective products and their flowing out of the factory. Dealing with such issues may require a considerable amount of expense and time.
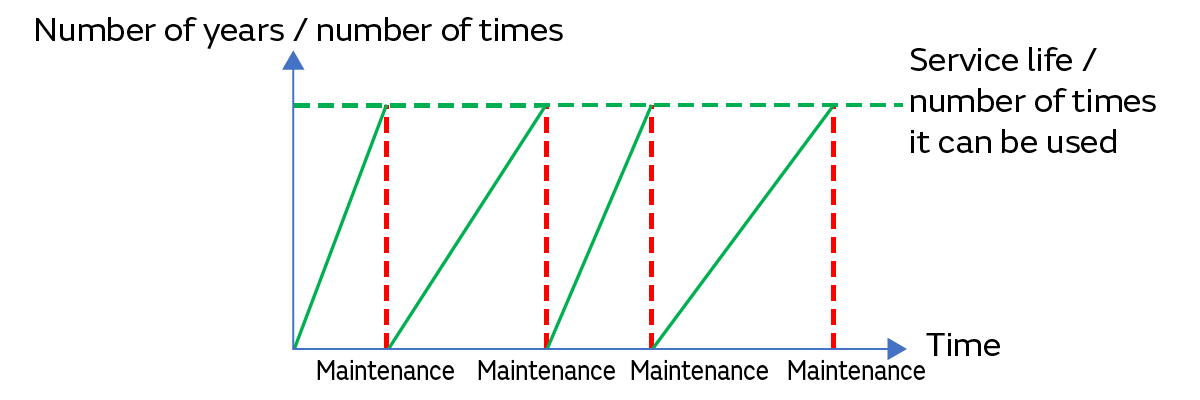
This is maintenance that is performed based on a piece of equipment’s service life, the number of times it is used, its condition, or other factors. It is also called “time-based maintenance” (Fig. 3).
Advantages:
The maintenance work is performed once a certain period has been reached. Therefore, it is possible to prevent failures and malfunctions from occurring in equipment. It is an effective maintenance method when the service life of each component used in equipment or the number of times those components are used can be grasped accurately.
Disadvantages:
It is necessary to establish criteria to ascertain as accurately as possible the life of components. Maintenance may be performed after a failure if the criteria is not accurate. Conversely, component and time losses may arise such as from the replacement of components that can still be used.
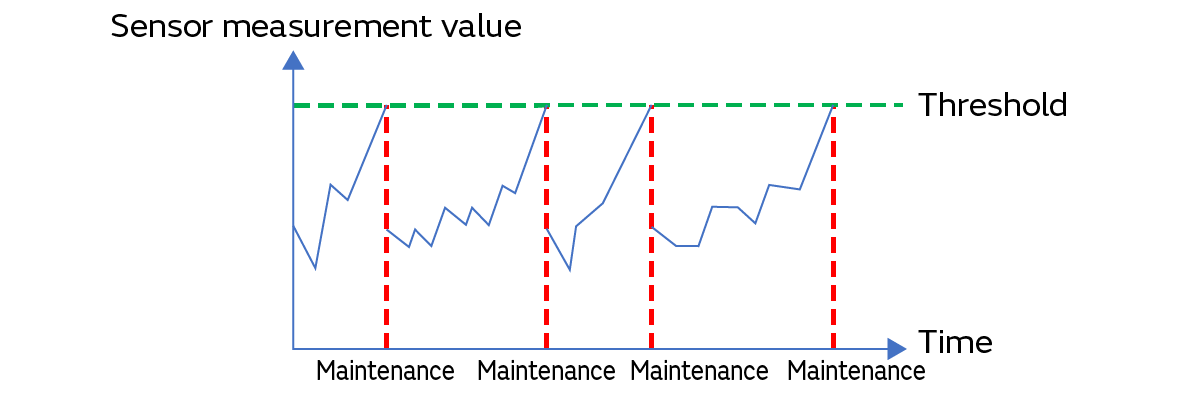
This is maintenance that is performed in line with extent of a piece of equipment’s deterioration by constantly monitoring its condition. It is also called “condition-based maintenance” (Fig. 4).
Advantages:
The maintenance work is performed when the equipment deteriorates. Therefore, it is possible to reduce component and time losses such as from the periodic stoppage of equipment for maintenance and the replacement of components that can still be used. Of course, it is also possible to prevent failures and malfunctions that would lead to the equipment stopping unexpectedly.
Disadvantages:
It is essential to have equipment to constantly monitor the condition of equipment and to store the collected data. Specifically, the constant monitoring of equipment requires a large number of various types of sensors. In addition, data loggers and similar recording devices are needed to store data. Furthermore, it is necessary to have equipment and other technologies to connect to those recording devices to communicate the data.
The most common method of maintenance currently is preventive maintenance whereby equipment is periodically maintained by determining the inspection timing based on the service life of each component used in equipment or the number of times those components can be used. Furthermore, there are an increasing number of cases in which semi-predictive maintenance is being adopted. This is when a large number of sensors that measure vibrations, temperature, current, voltage, and other elements are attached to equipment and thresholds are then set for each of them with maintenance being performed when those upper or lower limits are exceeded. In fact, a survey conducted on companies engaged in converting regular factories into smart factories produced results showing that over 96% of them cited “equipment maintenance utilizing sensors and AI” as the reason they are continuing to convert their factories into smart factories (Fig. 5).
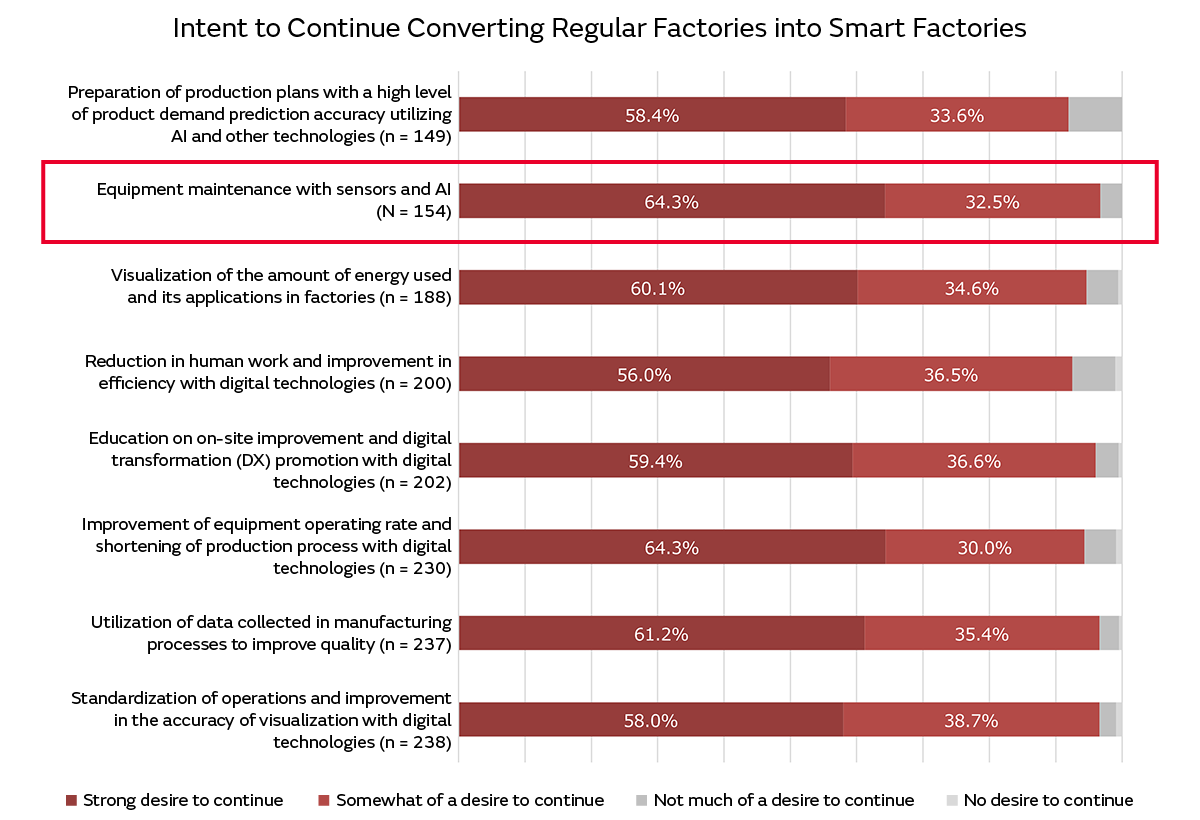
* About the survey:
Surveying entity: Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd.
Survey focus: 11,084 workers in the manufacturing industry in Japan (screening survey) / 500 workers in the manufacturing industry involved in converting their company’s regular factories into smart factories (main survey)
Survey method: Internet survey
Survey period: 3 days from January 25 (Wed.) to 27 (Fri.), 2023
* The total values may not necessarily match due to rounding.
In this way, equipment maintenance is currently undergoing a switch from preventive maintenance to predictive maintenance. We explain here the four technologies that can help with this switch from preventive maintenance to predictive maintenance.
Predictive maintenance begins with constant monitoring of the condition of equipment. There are individual differences in judgment when this monitoring is performed with the eyes and touch of people. This means it is not possible to respond accurately. We can quantify the condition of equipment by introducing sensors. Visualizing and analyzing the data collected from those sensors then enables us to respond more accurately. However, this requires installing many types and a large number of sensors in large factories. Accordingly, routing and connecting the sensor wiring requires many man-hours when changing the setup. Therefore, it is best to have noise-resistant sensors capable of wireless communication with a long transmission distance.
Moreover, devices have been developed that can keep a log of the actions taken by workers on manufacturing lines in recent years. It is also possible to record how those workers respond when trouble occurs. Utilizing these records allows various matters to be saved as data, including the deterioration of equipment that occurs on the manufacturing line and the actions taken by workers in response. This data can be used to give hints to improving processes in addition to maintenance.
Sensor fusion is a technology that realizes cognitive functions that cannot be obtained with a single sensor on an engineering basis. Specifically, sensor fusion has already been introduced into Advanced Driving Assistant Systems (ADAS). For instance, examples include reading the shapes of people, obstacles, and other objects with an image sensor and temperature sensor and then measuring the distance with a radar sensor utilizing milliwaves and microwaves to grasp the situation in the direction in which those objects are moving. It has also become possible to display warning messages on monitors in vehicles and to apply brakes automatically. This utilizes sensor fusion as a technology to, for example, automatically determine the situation with data collected from multiple sensors such as image sensors and radars and to then convey those results to the driver.
When we use this technology in equipment maintenance, we can analyze the measurement data from vibration sensors, temperature sensors, current sensors, and voltage sensors on an integrated basis. For example, if a current or voltage value is abnormal despite the motor vibrations and temperature being normal, we can determine that there has been a problematic change to the load on the part where the motor is operating. In addition, if an abnormal value is seen only in a vibration sensor, it is likely to be bearing wear, shaft deformation, level abnormality, or similar (Fig. 6).
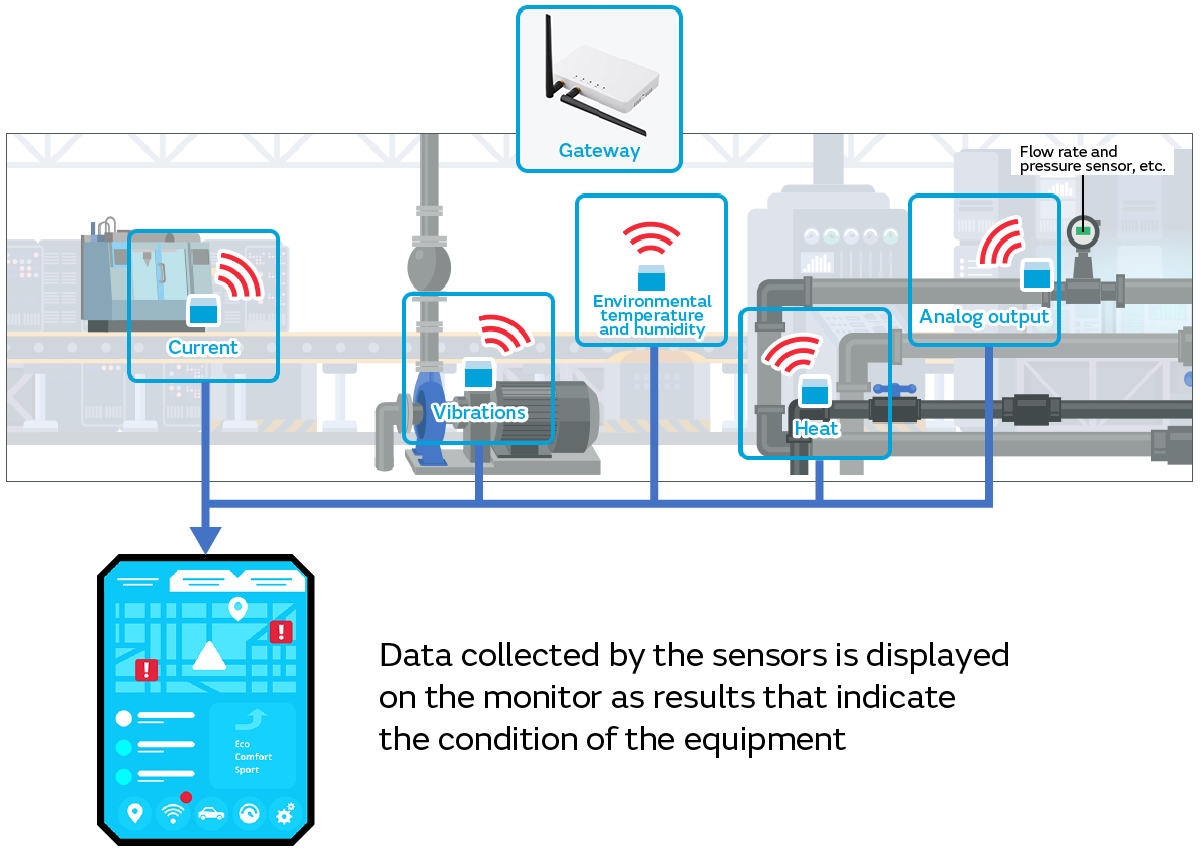
Conventionally, such abnormalities were grasped and determined by workers reading each sensor value and then comparing those values with their past experiences.
However, if we use the technology of sensor fusion, we can aggregate data collected by many sensors and display it on monitors or other devices as results that indicate the condition of equipment. This allows even inexperienced workers to accurately grasp the condition of equipment.
Sensor fusion is an outstanding technology. However, as the number of sensors increases and measurements become more precise, the amount of data increases. This leads to calculations becoming complex. It also becomes difficult to output data that indicates accurate results. Accordingly, the introduction of deep learning into equipment maintenance has come to be seen as important.
Introducing the AI technology of deep learning into equipment maintenance enables data collected from multiple sensors to be integrated and analyzed by AI. If there is an error in the output results, it is corrected through machine learning. Furthermore, accurate results are produced.
When we utilize AI in equipment maintenance, we become able to respond correctly to the condition of equipment that is constantly changing with self-learning such as by comparing the data collected during normal times and data collected from sensors to extract the difference in addition to simply detecting abnormalities that are determined by establishing a threshold (Fig. 7).
In this way, introducing AI into equipment maintenance doesn’t just reduce the differences in judgments due to differences in the proficiency level of the workers; we can also solve issues in conventional maintenance activities that rely on manpower, which involves investing a lot of personnel and hours in work, including monitoring and inspections.
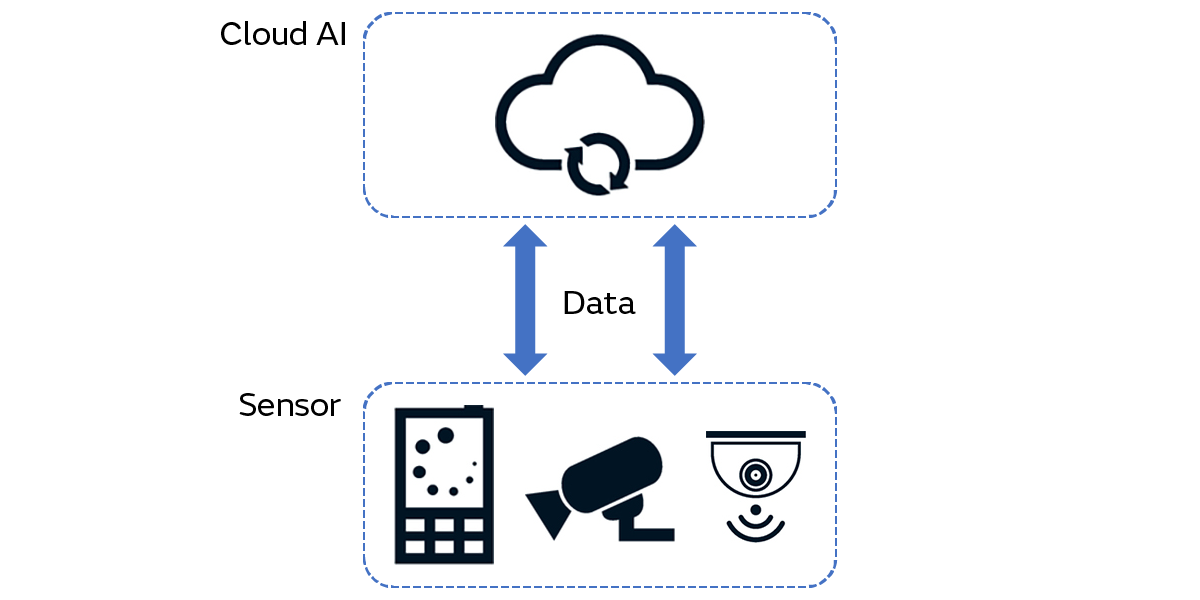
Edge AI is a technology that applies edge computing to AI. In edge AI, AI processing is performed with various sensors, cameras, mobile terminals, and other edge devices at the end of networks (Fig. 8). On the other hand, in contrast to edge AI, there is a technology called “cloud AI.” This is a technology that applies cloud computing to AI. This means AI processing is performed on the cloud server connected to the network and the results are then returned to the edge devices.
If we compare edge AI and cloud AI, we find that there are advantages to edge AI. These advantages include outstanding response speed and data confidentiality because the AI processing is performed on edge devices without involving a network. This also means edge AI is not impacted by the quality of the network.
High data confidentiality is an absolute requirement especially for equipment maintenance that handles data in factories. Moreover, a high response speed is sought in vibration and acceleration calculations, which require data collection at high sampling cycles. Therefore, we can say that edge AI is an attractive technology for predictive maintenance involving the handling of large volumes of data.
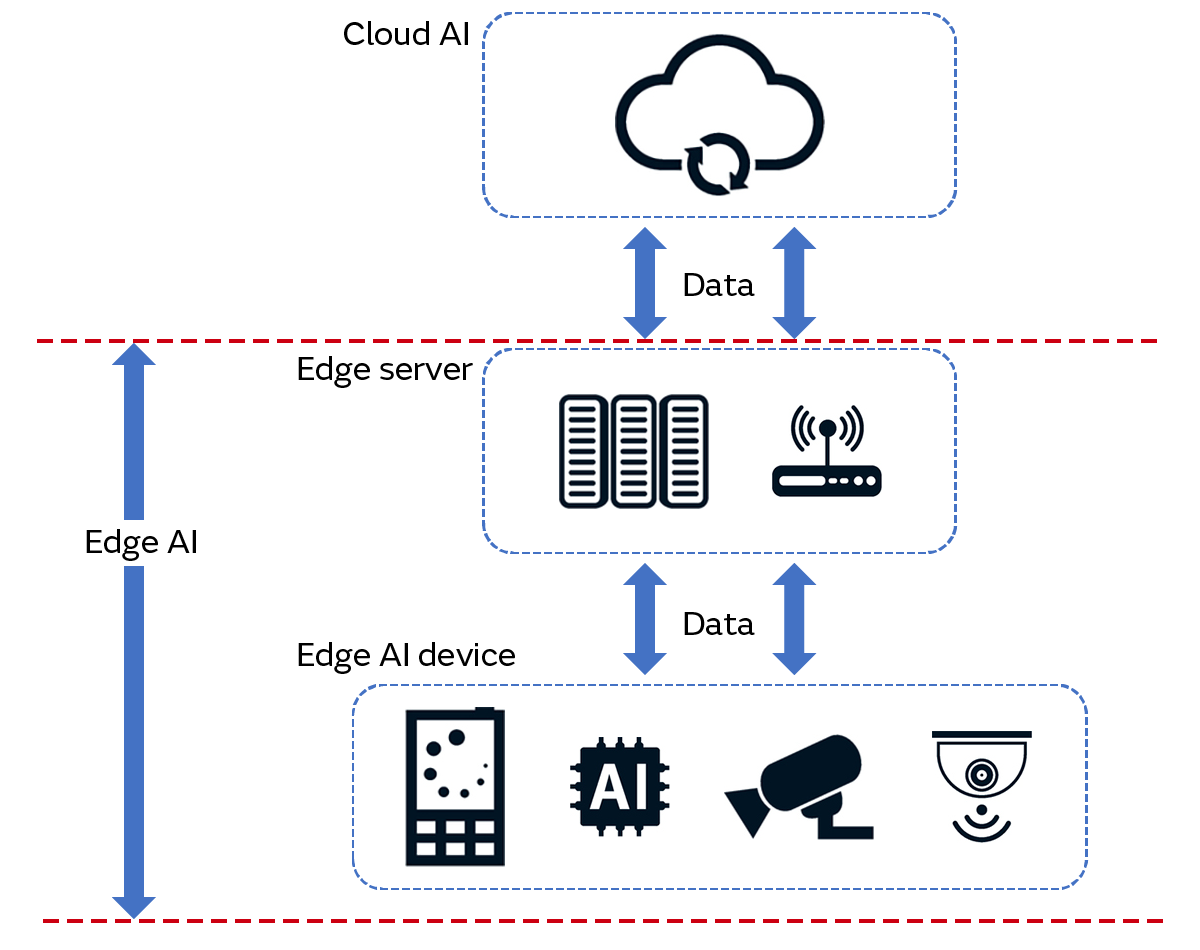
However, edge devices equipped with edge AI are small. This means they have disadvantages such as inferior memory size and calculating capacity compared to cloud AI. Accordingly, it is necessary to select either cloud AI, edge AI, or to use both together according to your purpose.
The importance of equipment maintenance for the stable operation of manufacturing lines has long been recognized. Nevertheless, on the other hand, it is also true that too much emphasis on production has led to daily maintenance activities being neglected.
Nowadays, with the globalization of manufacturing having long since progressed, manufacturing lines are continuing to constantly supply products to supply chains. In particular, supply chain management has been built based on production output during normal operations in regular factories that are being converted into smart factories. Under these circumstances, unexpected equipment failures on the manufacturing line can deal a major blow to the supply chain and cause damage to a company’s image.
Moreover, the introduction of sensor fusion, AI, and other technologies into equipment management is not just about optimizing equipment maintenance, reducing personnel expenses, and solving labor shortages. It is a cutting-edge approach with many advantages including the continuing maintenance of high productivity, the optimization of energy usage, and the effective utilization of personnel.
It is no exaggeration to say that realizing predictive maintenance by introducing sensor fusion, AI, and other technologies into equipment maintenance is the key to future corporate management for the manufacturing industry, which is surrounded by a complex economic environment such as the widening of supply chains.