BLF03VK221SNG

Noise suppression technologies/case study introduction (Consumer)
INDEX
Wi-Fi 6 is compatible with the 2.4 GHz band and 5 GHz band, but when noise (DC-DC converter switching noise, etc.) in the 0.1 GHz to 1 GHz range is applied to the front end of the 2.4 GHz band, third-order intermodulation distortion that interferes with the 5 GHz band occurs.
Communication disturbances occur if this is transmitted to the front end of the 5 GHz band through power lines, etc.
If using a base unit, communication with devices that use a 2.4 GHz band Wi-Fi may be the reason. For wireless units, simultaneous use with Bluetooth® may be the reason.
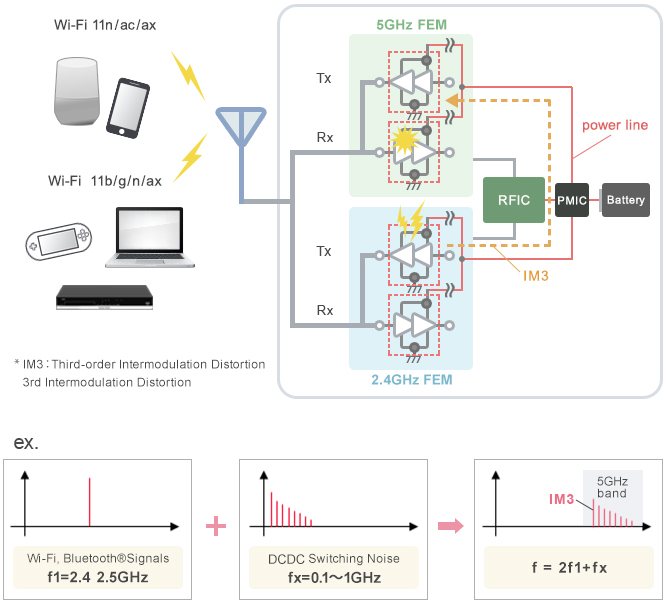
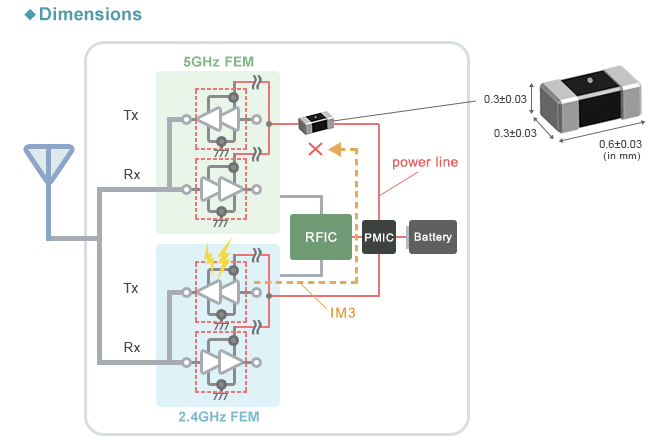
A noise filter that supports the 5 GHz band is applied to prevent noise entry in the 5 GHz band. The BLF03VK is a noise filter that was designed for effective removal of noise in the 5 GHz band.
Inserting the BLF03VK series into the power line can prevent third-order intermodulation distortion from flowing into the front end of the 5 GHz band.
BLF03VK Series
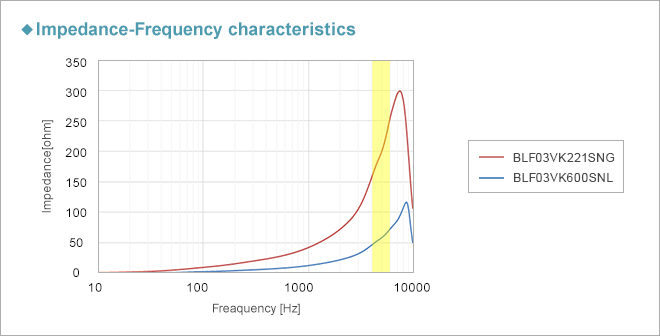
| Murata Part Number |
Impedance@5GHz(ohm) | Rated Current (mA) @85℃ |
Rated Current (mA) @125℃ |
DC Resistance (ohm max.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 220 +/- 40% | 800 | 500 | 0.155 | |
| 60 +/- 40% | 1200 | 780 | 0.065 |
BLF03VK221SNG
A compact (0.6 x 0.3 mm) noise filter that specializes in noise suppression in 5 GHz band which is one of the communication frequencies of Wi-Fi (wireless LAN).
BLF03VK600SNL
This BLF03VK series is the first noise filter with specifications that guarantee impedance values for the 5 GHz band.
Equipping high speed interfaces can also lead to reception sensitivity deterioration.
As Wi-Fi communication becomes faster, the speed of internal data transmission interfaces will also increase, and frequencies that will interfere with Wi-Fi signals will also be processed.
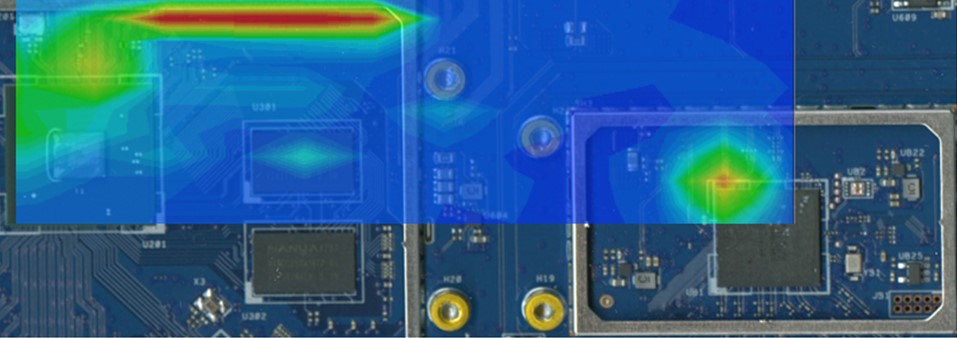
For this reason, PCI Express signals are radiated and the 2.4 GHz band Wi-Fi reception sensitivity deteriorates.
Also, due to the popularity of USB Type-C connectors, support for USB 3.1 has progressed, and due to the USB 3.1 having a signal frequency close to the 2.4 GHz band, there are examples that lead to Wi-Fi reception sensitivity deterioration.
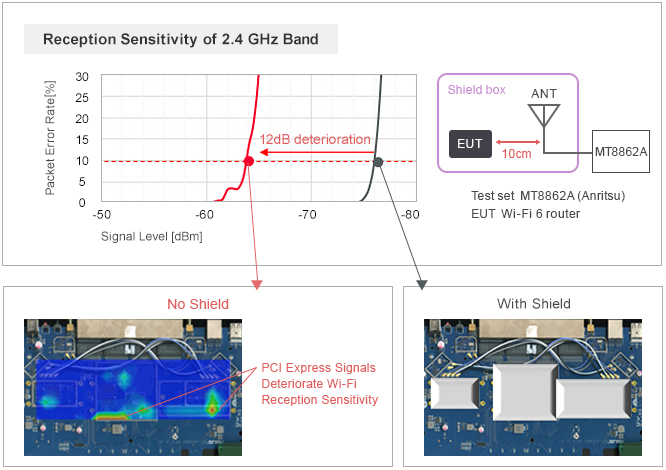
A noise filter is to be inserted on the interface signal line to eliminate noise that interferes with Wi-Fi from high speed interfaces.
However, since these interfaces use high speed signals, you are required to select those that do not affect signal waveforms.
In principle, common mode choke coils/common mode noise filters (CMCC) do not affect differential signals, but since there are differential mode impedances in actual products to some extent, you are required to select applicable parts.

(PCI Express gen3, USB3.1 gen1, HDMI2.1 etc.)
(PCI Express gen3, USB3.1 gen2, HDMI2.1 etc.)
⇒Measures can be taken by inserting the BLF03VK series to the power line
⇒Measures can be taken by using common mode choke coils/common mode noise filters that support high speed signals on the high speed interface signal line
| BLF03VK Series | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stock Check | Impedance (@5GHz) | Rated current (@85℃) | Rated current (@125℃) | DC resistance (max) | |
 |
220±40% | 800 | 500 | 0.155 | |
 |
60±40% | 1200 | 780 | 0.065 | |
| For 2.4 GHz Band Noise Suppression Measures | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stock Check | CM Impedance (@100MHz) | Rated current | DC resistance (@max) | DC resistance (Rdc) | |
 |
28 | 130 | 2.375 | 1.9±25% | |
 |
35 | 120 | 2.875 | 2.3±25% | |
 |
15 | 100 | 3.125 | 2.5±25% | |
| For 5 GHz Band Noise Suppression Measures | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stock Check | CM Impedance (@100MHz) | Rated current | DC resistance (@max) | DC resistance (Rdc) | |
 |
12 | 160 | 1.5 | 1.2±25% | |
 |
12 | 150 | 2 | 1.6±25% | |
 |
5 | 100 | 1.625 | 1.3±25% | |







