Noise suppression technologies/case study introduction (Automotive)
Example of noise suppression in the power circuits of devices mounted in vehicles - Investigation of noise conditions
Investigation of noise conditions
The initial noise conditions were confirmed and the types of noise were isolated.
Noise was measured for the following three patterns.
- Conducted noise (150 kHz to 108 MHz)
- Radiated noise (150 kHz to 30 MHz)
- Radiated noise (30 kHz to 300 MHz)
Confirmation of noise conditions without measures to suppress noise
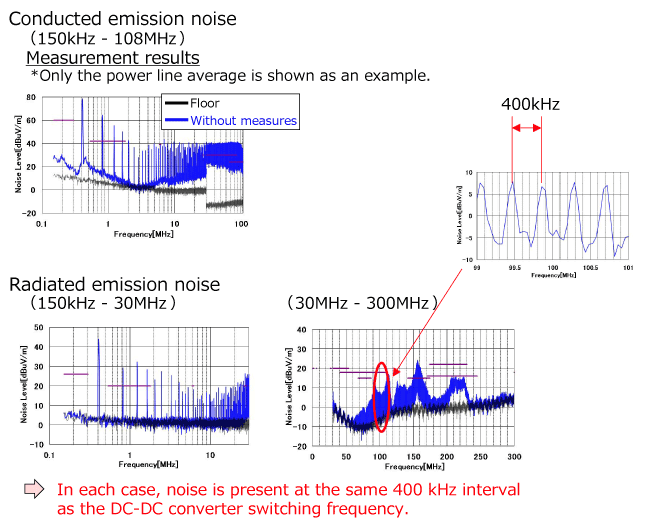
Investigation of conduction mode of problematic noise (1) - Conducted noise -
The conduction mode (common mode or normal mode) of problematic conducted noise was investigated.
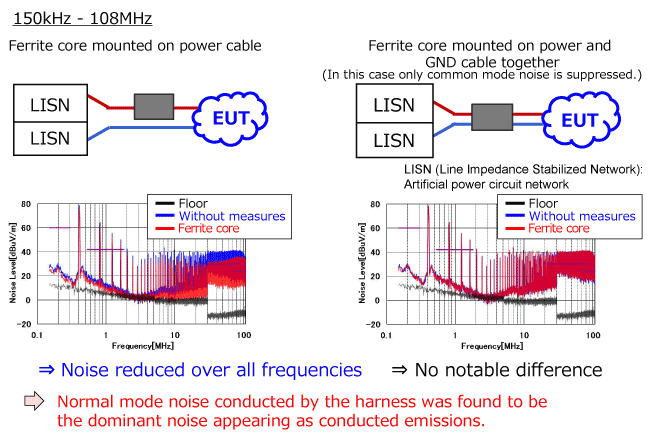
Investigation of conduction mode of problematic noise (2) - Radiated noise (150 kHz to 30 MHz) -
The conduction mode (common mode or normal mode) of problematic radiated noise was also investigated. (150 kHz to 30 MHz band)
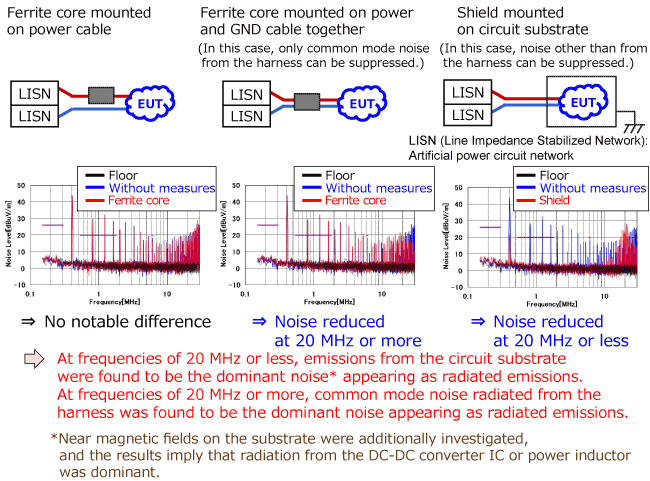
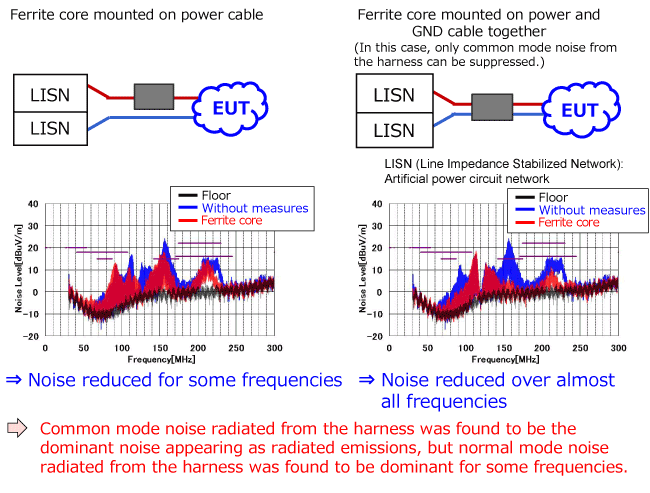
Investigation of conduction mode of problematic noise (3) - Radiated noise (30 MHz to 300 MHz) -
The conduction mode (common mode or normal mode) of problematic radiated noise was investigated. (30 MHz to 300 MHz band)