Inductors

Inductor Guide
Inductors have many different uses, and a variety of product types are available according to the application.
Murata Manufacturing offers a diverse lineup of chip inductors classified by application into the three types of inductors: high-frequency circuits; power supply line inductors (power inductors); inductors for general circuits.
This article describes inductors for high-frequency circuits.
As the name implies, inductors for high-frequency circuits are used in the high-frequency band from 10 MHz to several GHz. As these products require a high Q (Quality factor) value, most have a non-magnetic core structure, and they are mainly used in the high-frequency circuits of mobile communications equipment, such as mobile phones, wireless LAN, and others.
Application | Location | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
Matching | Lines between components in | Eliminating impedance mismatch and |
Resonance | Synthesizers and oscillation | Securing the required frequencies |
Choke | Power supply lines of functional | Cutting AC currents such as high- |
Table 1 Examples of inductor applications in each circuit block of a mobile phone
Murata Manufacturing offers a diverse lineup of inductor products for high-frequency circuits with three different structures: wire wound, multilayer and film.
The features and suitable applications of each structure are briefly described below.
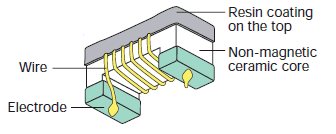
The wire wound structure is formed by winding copper wire in a spiral shape around an alumina core. The coil can be formed using thicker wire than the multilayer and film structures, which provides the following features:
1) Low DC resistance is possible
2) Extremely high Q (Quality factor) value
3) Large currents can be supported
These features make the wire wound structure suitable for matching applications in antenna and PA circuits that require an extremely highQ factor, and resonance applications in IF circuits.
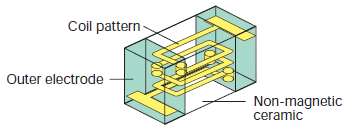
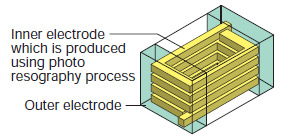
The multilayer structure is formed by layering ceramic materials and a coil conductor to create an integrated multilayer-type inductor. This enables a smaller size and lower cost compared to the wire wound structure.
While the Q factor is lower than that of the wire wound structure, the multilayer structure provides good overall balance between the L value deviation, rated current, size, price, and other characteristics, enabling use in a wide range of applications.
The multilayer structure is suitable for various applications such as RF circuit matching, choke, and resonance for mobile communication equipment.
Film structure chip inductors have a multilayer structure, but the coil is formed with high accuracy over ceramic materials using Murata's original micro-processing technology.
Extremely accurate cores can be formed, providing the following features:
1) High-performance electrical characteristics can be realized even for compact chips such as 0603 size
2) Stable inductance and small inductance value steps are supported
3) High Q and high SRF
This makes film structure chip inductors suitable for RF circuit matching and resonance applications that require narrow deviation and a high Q factor to support trends toward smaller and more lightweight mobile communication equipment.
As described above, inductors for high-frequency circuits are used in various RF circuits by making effective use of the features of each type. The next article will introduce the structures and suitable applications of inductors for power circuits.
*The information presented in this article was current as of the date of publication. Please note that it may differ from the latest information.