Noise suppression technologies/case study introduction (Consumer)
Audio line noise suppression for smart phones:(2) Countermeasures
*Click to move to each item.
INDEX
Class D amp noise suppression
Filterless Class D amplifiers are used to amplify the audio signal in smart phones.
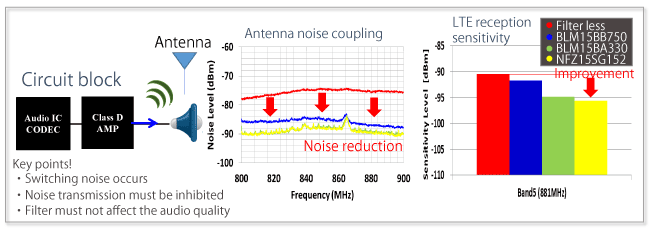
These filterless Class D amplifiers do not require an LC filter for audio demodulation, which allows them to be arranged in a small-scale circuit that connects just the amp and the speaker. However, processes that amplify the signal generate switching noise, which is emitted into the surrounding space, and cause a loss of reception sensitivity through coupling with its own antenna.
Because this creates noise, we would like to use a different type of amplifier. However, the filterless Class D amplifiers are essential due to their miniature size and superior efficiency, which make it possible to reduce smart phone power consumption.
Figure 1 shows an example in which noise has coupled (interfered) with the antenna, and we can see high levels of noise within the cellular band.
Using the NFZ15SG audio line noise filter reduces the noise level and improves the reception sensitivity, depending on the reduced level. The newly developed NFZ series possesses superior impedance characteristics in the cellular band that are effective for improving reception sensitivity.
Speaker, earphone isolation countermeasures

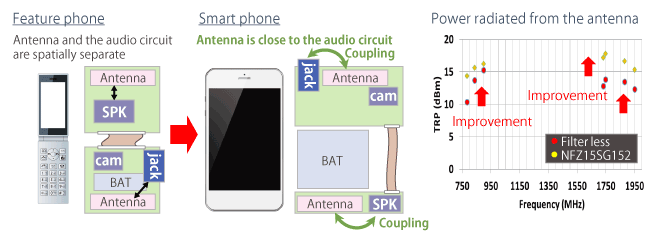
In order for the antenna to efficiently emit radio waves, the antenna itself must be separate.
However, in practice, electronic circuits are configured around and integrated with the antenna, which degrades the characteristics of the antenna.
The following two methods can be considered as countermeasures.
- Physically separate the audio circuit from the antenna.
- Electrically separate the two elements (isolation).
Due to the increasing circuit density of smart phones in recent years, method (1) is difficult to adopt, which means that the components must be electrically isolated, as in method (2).
In order to achieve isolation, it is important to increase the impedance of the integrated pathways or the circuit junction to make it seem as if the circuits are not connected at all.
Figure 2 shows an example of applying such a countermeasure to the earphone junction. (The measurement result TRP indicates the magnitude of the power radiated by the antenna.)
Using a high impedance audio line noise filter (NFZ Series, LQW Series) in the cellular band ensures isolation and improves the efficiency of radio wave emission compared to the antenna without the countermeasures.
Microphone TDMA countermeasures

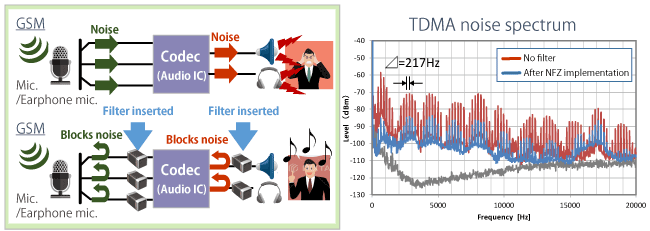
Because the sound picked up by the microphone is subtle, it is amplified by the LNA (low noise amplifier) built into the codec and detected as sound. The LNA receiver is typically high impedance, which means that RF signal interference from wireless communication is detected as a large voltage.
In particular, RF signals are detected in the voice band during GSM communication, which can cause a buzzing noise to occur in the caller’s speaker and receiver as well as in the receiver of the other party. (Keyed carrier noise) This is a characteristic of the method used in GSM communication. Because the standard specifies power emissions as high as 33 dBm at 4.6 ms intervals, the 217 Hz frequency component is heard as sound, and countermeasures for this problem are still needed around the world.
In this countermeasure, a filter with high impedance in the communication band that does not affect the sound is an effective way to prevent RF signal interference.
As shown in Figure 3, a large spectrum of noise is detected in the audible range (20 Hz to 20 kHz) when a filter is not inserted, while the use of an NFZ15SG audio line filter is able to significantly reduce the noise level.
Audio line filter item list
As explained above, it is important to avoid degrading audio quality while satisfying the target characteristics for noise level and reception sensitivity in audio line noise and isolation countermeasures.
In order to satisfy both requirements, Murata offers the NFZ and LQW series of audio line noise filters.
Adopting these audio line countermeasure components enables manufacturers to design smart phones equipped with miniature, high-quality audio circuits.
NFZ series 
| Product name | Stock Check | Impedance at900MHz(Ω) |
Impedance at1.7GHz(Ω) |
DC resistance(Ω) | Rated current(A) | Product size (max. height) (mm) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Typ. | Min. | Typ. | Typ. | ||||
| NFZ15SG101SN11 |  |
100 | 70 | 160 | 0.07 | 1.1 | 1.0x0.5 (0.55) |
| NFZ15SG151SN11 |  |
150 | 100 | 250 | 0.09 | 1.0 | |
| NFZ15SG331SN11 |  |
330 | 230 | 540 | 0.2 | 0.65 | |
| NFZ15SG771SN10 |  |
770 | 530 | 900 | 0.35 | 0.5 | |
| NFZ15SG152SN10 |  |
1500 | 1000 | 1200 | 0.55 | 0.4 | |
| NFZ15SG262SN10 |  |
2600 | 1800 | 1450 | 0.8 | 0.35 | |
| NFZ15SG462SN10 |  |
4600 | 2800 | 1800 | 1.25 | 0.27 | |
| Product name | Stock Check | Impedance at100MHz(Ω) |
DC resistance(Ω) | Rated current(A) | Product size (max. height) (mm) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Typ. | 85℃ | 125℃ | ||||
| NFZ18SM121SN10 |  |
120±25% | 0.11 | 1.25 | 1.1 | 1.6x0.8 (0.95) |
| NFZ18SM251SN10 |  |
250±25% | 0.15 | 1.1 | 1.0 | |
| NFZ18SM501SN10 |  |
500±25% | 0.2 | 0.95 | 0.85 | |
| NFZ18SM701SN10 |  |
700±25% | 0.23 | 0.8 | 0.8 | |
Audio line noise suppression

(2) Countermeasures