Noise suppression technologies/case study introduction (Consumer)
Audio line noise suppression for home audio:(1) Audio line
*Click to move to each item.
INDEX
Noise problems in home audio
In the past, analog amplifiers were used in high output audio equipment to emphasize audio quality, but in recent years, digital amplifiers have improved in terms of audio quality and have become popular in home audio as well.
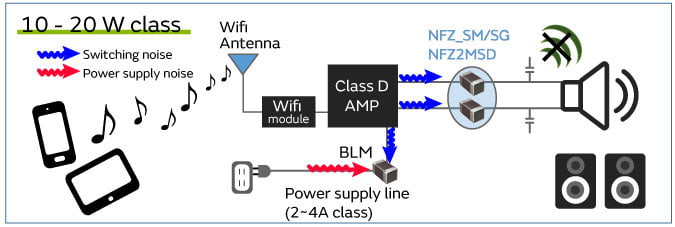
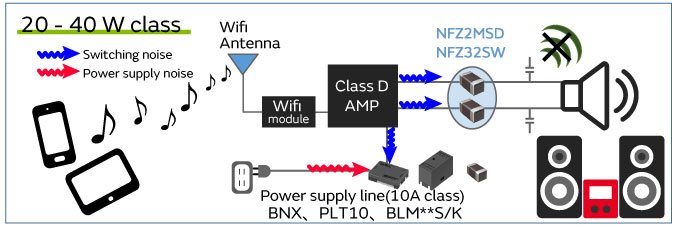
Due to the switching noise that occurs in digital amplifiers, noise that exceeds the EMC standards can be emitted into the space around the cable connected to the speaker. Noise suppression using capacitors and inductors is implemented to solve this noise problem.
* EMC standards: Noise regulation standards prescribed by various countries (examples include VCCI in Japan, the FCC in the United States, and the EN standards in Europe)
Murata is commercializing the NFZ series of audio line filters as noise filters that can suppress unwanted noise while maintaining audio quality. This section introduces noise problems in home audio and their solutions.
Audio line problems in home audio
Inductors are generally introduced as EMI suppression components to suppress noise in electronic equipment.
To ensure high audio quality in home audio, low distortion noise suppression products are required for audio lines.
In some cases, noise suppression is also needed for the power supply line to satisfy EMC standards.
Power supply noise suppression
Figure 1 Home audio_Noise suppression product use cases by output class
Related knowledge
Noise suppression comparison with conventional ferrite beads
Audio distortion characteristics and noise suppression performance in audio line noise filters
<Audio distortion>* Basics of audio distortion
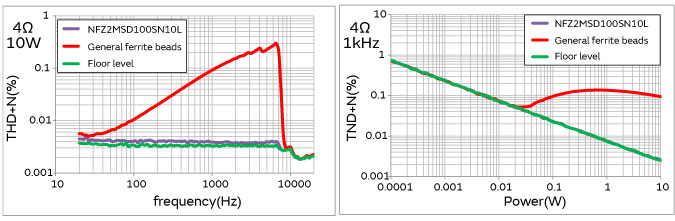
The audio distortion characteristics of common ferrite beads and the NFZ_SD audio line filter are shown in Figure 2.
While common ferrite beads exhibit high audio distortion, this does not occur in the NFZ_SD Series, which has impedance characteristics that do not change even when a large current is flowing. This makes it possible to achieve noise suppression while maintaining audio quality without a filter.
<Benefits of noise suppression>
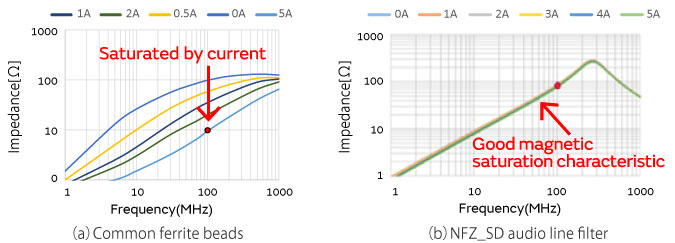
In the case of home audio, the speakers output very high volumes compared to smart phones and other mobile devices, so a large current (signal) flows through the noise suppression components. The characteristics of noise suppression products that use ferrite materials change when a current is flowing, so caution is necessary when making a selection.
As an example, Figure 3 shows the changes in impedance characteristics of a noise suppression product when a current is flowing. The left side shows the characteristics of ferrite beads with a rated current of 5 A, while the right side shows the Murata NFZ_SD Series. The impedance characteristics of the NFZ_SD Series do not change even when a large current is flowing, so they are able to maintain noise suppression performance. Because the volume output from a speaker is not constant, it is necessary to select a filter with impedance characteristics that do not fluctuate for noise suppression.
In addition, because the noise occurring in a digital amplifier has a spectrum of up to several 100 MHz, suppression products with a high impedance in that band are effective.
As shown above, the NFZ_SD Series of products provide effective noise suppression while maintaining audio quality.
Noise suppression examples
<Suppression Example 1: Impact of the speaker cable length>
In recent years, various types of speakers ranging from conventional large speakers to portable types are being sold.
The length of the speaker cable changes according to the size of the audio equipment, and the noise level also changes accordingly.
As an example, Figure 4(a) shows the radiation noise level measurement results when the length of the speaker cable is changed. As the length of the cable increases, the noise level radiating from the cable also increases, so noise suppression is essential to clear noise regulations.
Figure 4(b) shows the results after applying noise suppression. Noise regulations can be cleared by using the NFZ_SD audio line filter in the speaker line.
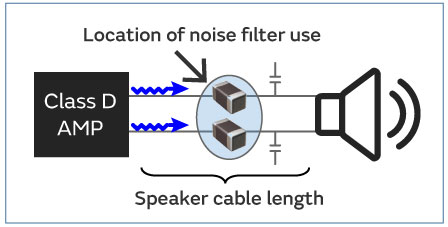
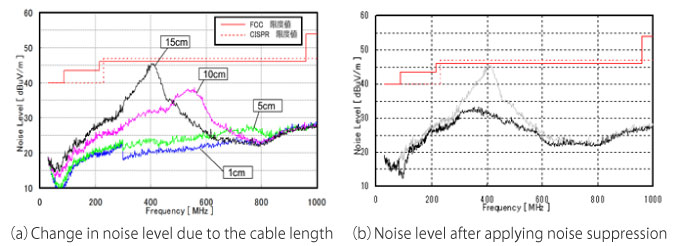
Figure 4 Block diagram of smart phone audio circuits
<Suppression example 2: Comparison with common ferrite beads>
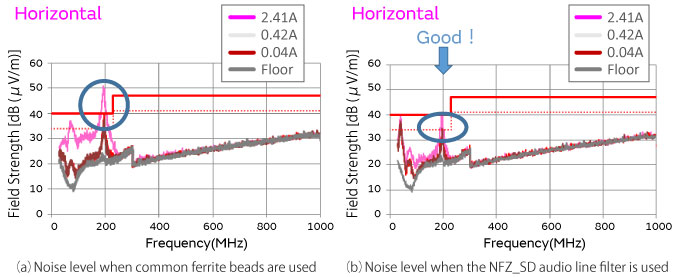
Figure 5 shows the results of measuring radiation noise when noise suppression is implemented in the Class D amplifier of a home audio device.
The Murata NFZ_SD audio line filter and common ferrite beads were used as suppression components.
While the NFZ_SD audio line filter exhibits significant noise suppression effects even when a large current is flowing, the noise suppression of common ferrite beads is insufficient when the current value is large (2.4 A), which results in noise radiation that exceeds the standard value.
This is due to the superposition characteristics of the component. The NFZ_SD Series is able to maintain effective noise suppression even when a large current is flowing, so it can be said to be effective for radiation noise suppression in the audio lines of home audio equipment.
Audio line filter item list
As explained above, it is important to avoid degrading audio quality while satisfying the target characteristics for noise level and reception sensitivity in audio line noise and isolation countermeasures.
In order to satisfy both requirements, Murata offers the NFZ and LQW series of audio line noise filters.
Adopting these audio line countermeasure components enables manufacturers to design smart phones equipped with miniature, high-quality audio circuits.
NFZ series
For high output audio (1 - 5 A class)
Product name | Stock Check | Impedance | DC resistance(mΩ) | Rated current(A) | Product size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Max | |||||
10±30% | 20 | 5.2 | 2.0x1.6 | ||
15±30% | 23 | 4.4 | |||
20±30% | 28 | 3.9 | |||
30±30% | 33 | 3.7 | |||
60±30% | 54 | 2.7 | |||
90±30% | 95 | 2 | |||
130±30% | 144 | 1.5 |
For medium output (1 - 2 A class)
Product name | Stock Check | Impedance | Impedance | DC resistance(Ω) | Rated current(A) | Product size |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
typ. | Max | |||||
3.2±30% | 300 | 0.036 | 2.55 | 3.2x2.5 | ||
6.8±30% | 900 | 0.054 | 2.05 |
Product name | Stock Check | Impedance | DC resistance(Ω) | Rated current(A) | Product size | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Max | 85℃ | 125℃ | ||||
120±25% | 0.14 | 1.25 | 1.1 | 1.6x0.8 | ||
250±25% | 0.19 | 1.1 | 1.0 | |||
500±25% | 0.25 | 0.95 | 0.85 | |||
700±25% | 0.29 | 0.8 | 0.8 | |||