Capacitor
Capacitor Guide
Final revision date: 12/1/2023
Greetings everyone.
This technical column describes the basic facts about capacitors.
This page describes "What is the temperature characteristics of ceramic capacitors?"
The temperature characteristics of ceramic capacitors are those in which the capacitance changes depending on the operating temperature, and the change is expressed as a temperature coefficient or a capacitance change rate.
There are two main types of ceramic capacitors, and the temperature characteristics differ depending on the type.
This type uses a calcium zirconate-based dielectric material whose capacitance varies almost linearly with temperature.
The slope to that temperature is called the temperature coefficient, and the value is expressed in 1/1,000,000 per 1°C (ppm/°C).
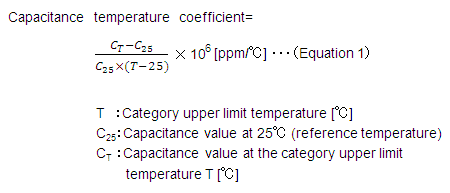
The temperature coefficient of capacitance is defined by Equation 1 from the capacitance value C25 at the reference temperature*1 and the capacitance value CT at the category upper temperature*2.
*1 Although the EIA standard is 25°C and the JIS standard is 20°C, the EIA standard of 25°C, which is the de facto standard, is used here as the standard.
*2 Maximum operating temperature: By design, maximum ambient temperature including self-heating 20°C MAX that allows continuous use of capacitors.
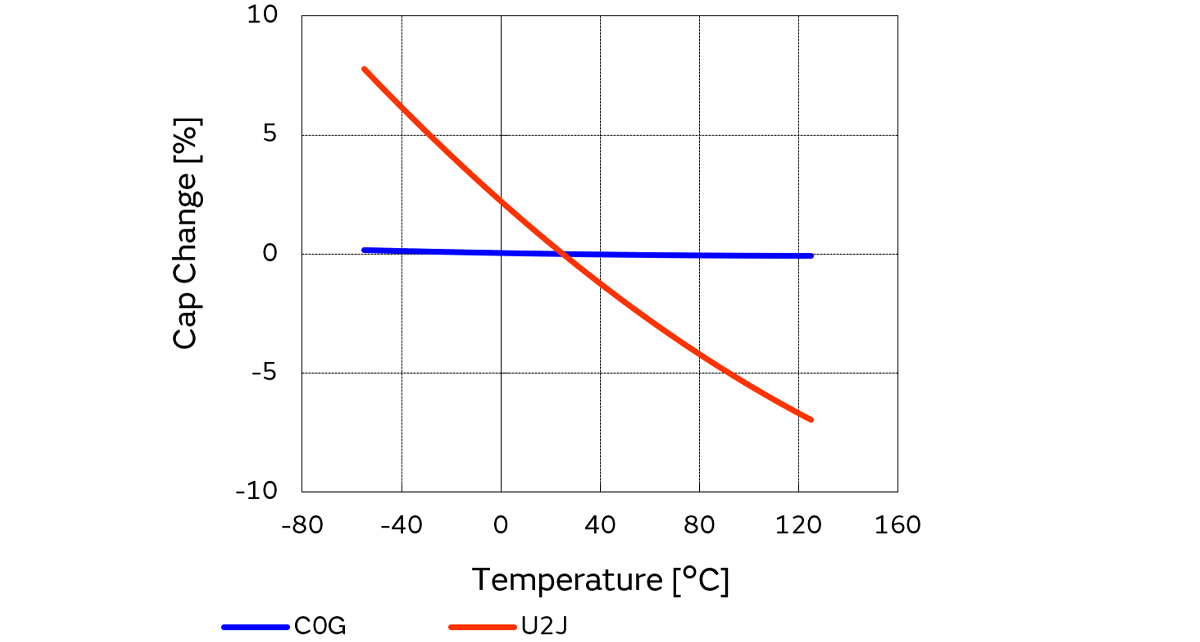
The EIA standard specifies various capacitance temperature factors ranging from 0ppm/°C to −750ppm/°C.
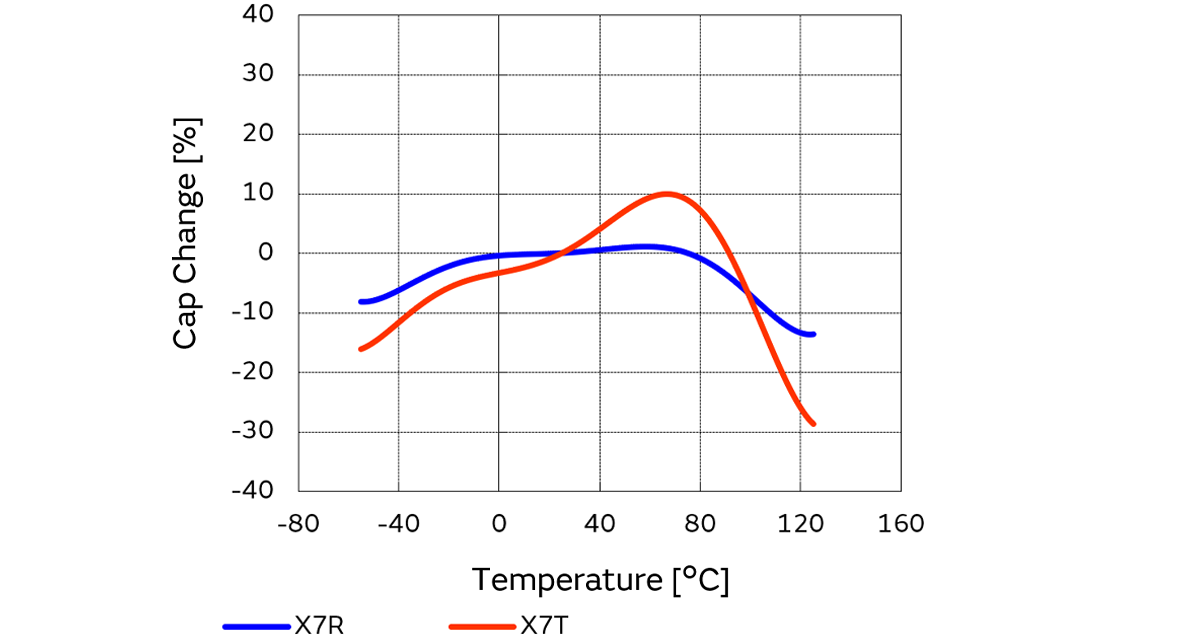
Figure 1 below shows typical temperature characteristics.
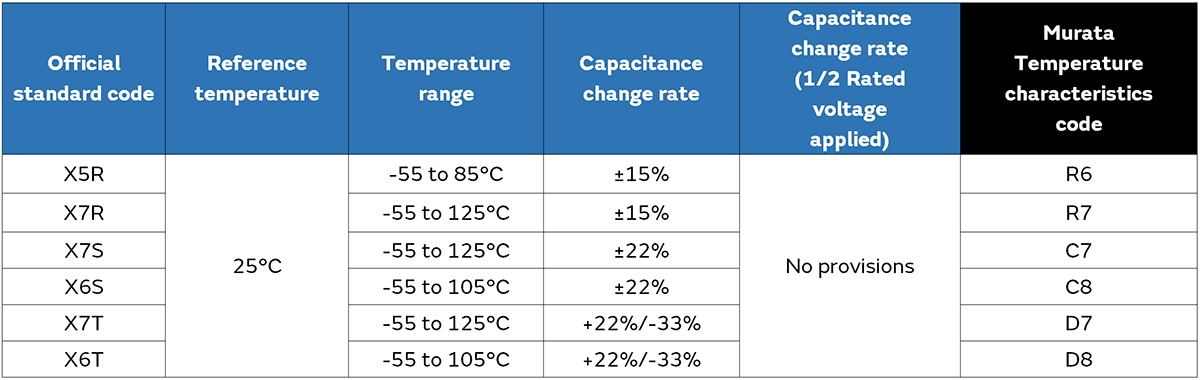
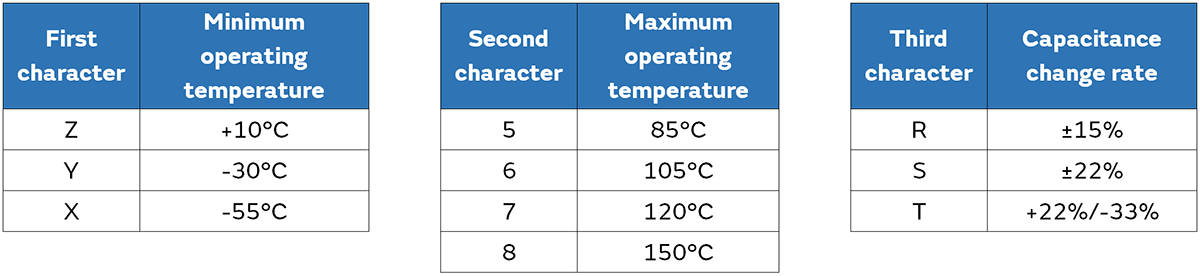
And the tables below show the excerpts of applicable EIA and JIS standards.
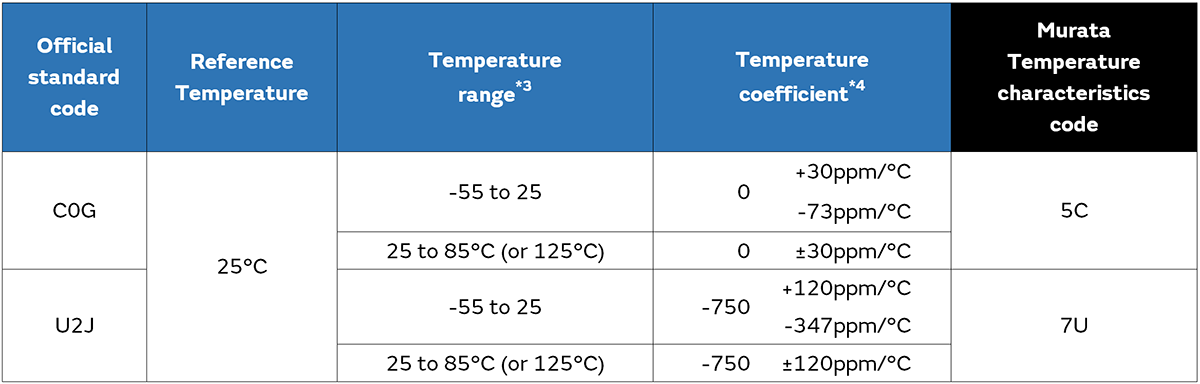
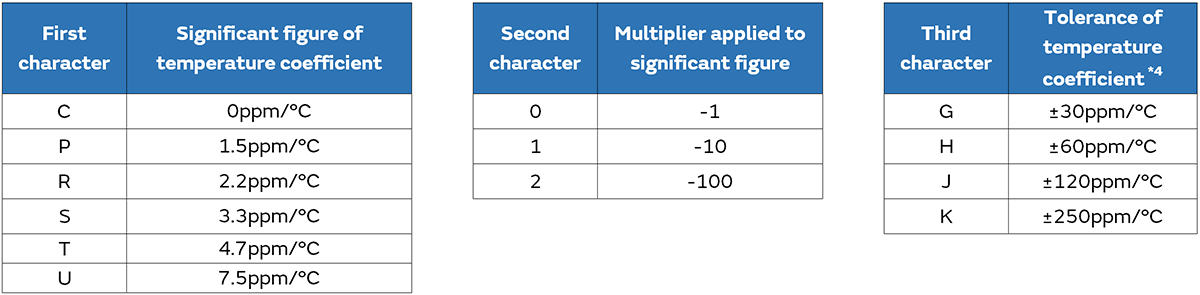
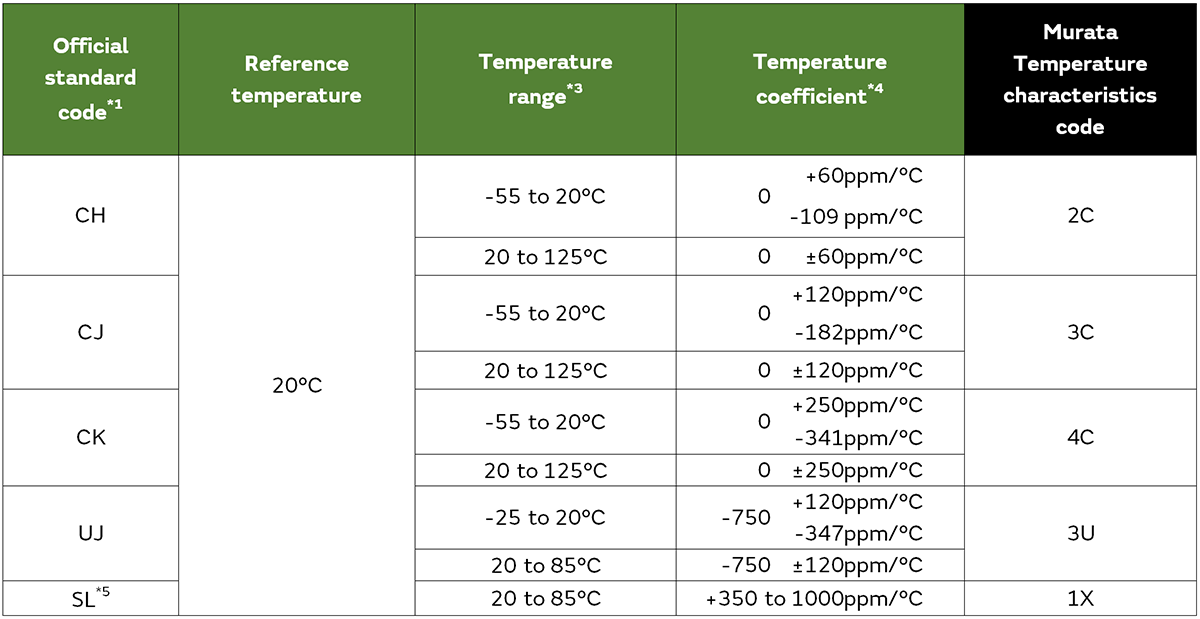
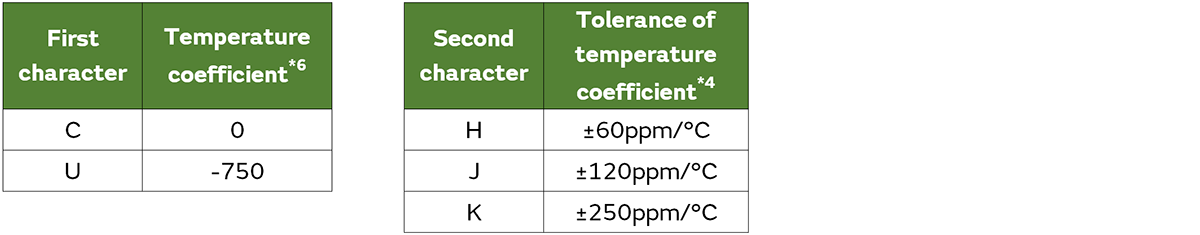
*3 It may differ from the latest JIS standard.
*4 The second character represents the tolerance of temperature coefficient between the reference temperature and the upper temperature range. The tolerance of temperature coefficient between the Reference temperature and the lower temperature range is calculated based on the EIA standard.
*5 Rules of official standard code does not apply to SL. Combining S and L means that the temperature coefficient is +350 to −1000ppm/°C.
*6 Temperature coefficient is divided into first and second character in EIA, and only first character in JIS.
This type uses barium titanate as the dielectric material, and the capacitance value exhibits irregular variance with respect to temperature.
For this reason, the electrostatic capacitance vs. temperature characteristic standard values are specified by the maximum and minimum values of the capacitance change rate within the applied temperature range, relative to the capacitance value C25 at the reference temperature*7. (See Equation 2.)
*7 Based on EIA standard of 25°C
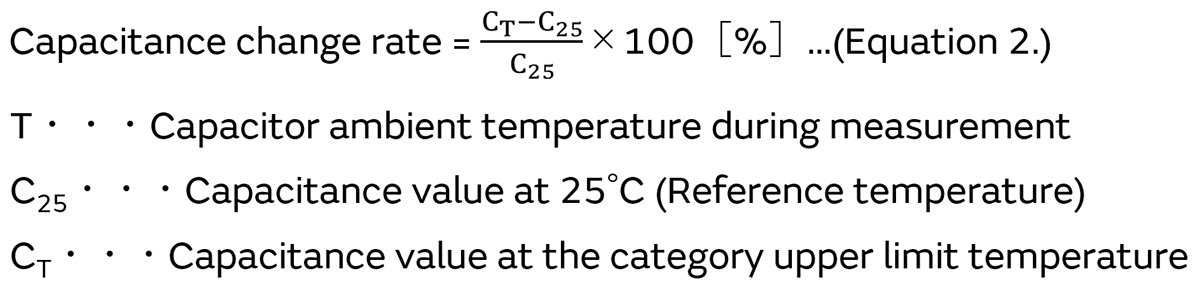
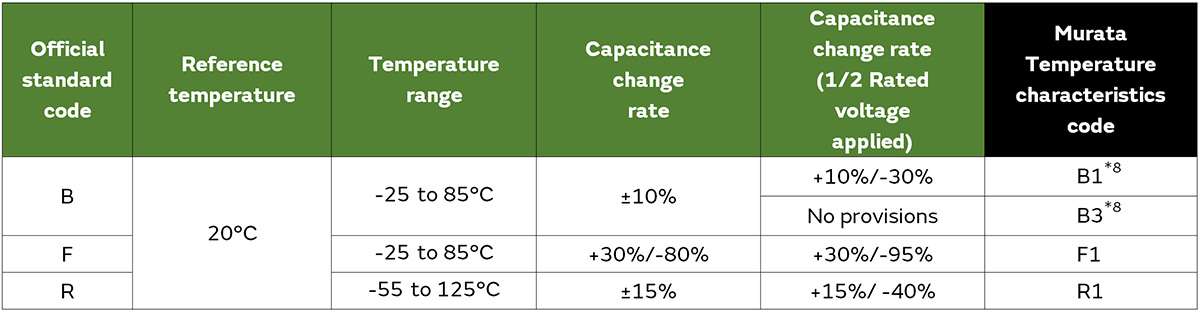
*8 The official standard code “B” of the temperature characteristic specified by JIS can individually determine the capacity change rate when voltage is applied. Murata defines capacity change as +10%/−30% in Code B1 and capacity change as No provisions in Code B3.
The information presented in this article was current as of the date of publication.
Please note that it may differ from the latest information.