Noise suppression technologies/case study introduction (Automotive)
Automotive Ethernet for ADAS Noise suppression measures for 1000Base-T1 (1)
INDEX
- Spread of Automotive Ethernet in Automobiles
- Signal Transmission by Automotive Ethernet
- Noise Issues in Automotive Ethernet
- Factors for Generation of Common Mode Noise
- Noise Suppression Measures for Automotive Ethernet
- Notes on CMCCs Used in Automotive Ethernet
- Measures for Preventing Conducted Emission
- Testing of Immunity (DPI) Measures
- Key Points for Testing of Immunity (DPI) Measures
- Conclusion
Production of some products (DLW32SH101XK2) introduced in this article has been discontinued.
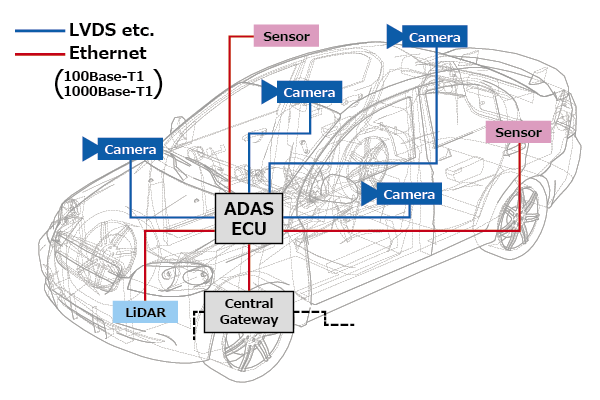
1. Spread of Automotive Ethernet in Automobiles
Today, various sensors and cameras are installed as devices for supporting advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). Although LVDS and other interfaces are being used for transfer of camera data, automotive Ethernet is being used in growing numbers of cases for transfer of LiDAR and other sensor data. Whereas standards such as 100Base-TX and 1000Base-T are being used for office environments, standards such as 100Base-T1 and 1000Base-T1 are specified for use in automobiles.
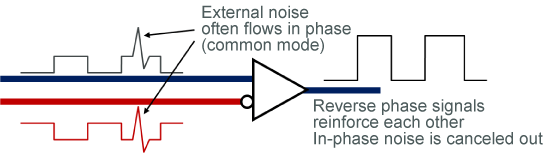
2. Signal Transmission by Automotive Ethernet
Ethernet and other automotive interfaces use differential transmission signals that have minimal emissions and are resistant to the effects of external noise. Because external noise often enters both differential transmission signal lines in the same way, this does not affect their difference, and these lines feature strong resistance to external noise. Another advantage is that, because the signal lines in the pair are adjacent to each other, any magnetic field generated by signal currents are canceled out, and so it is difficult for noise to be emitted externally.
For external noise
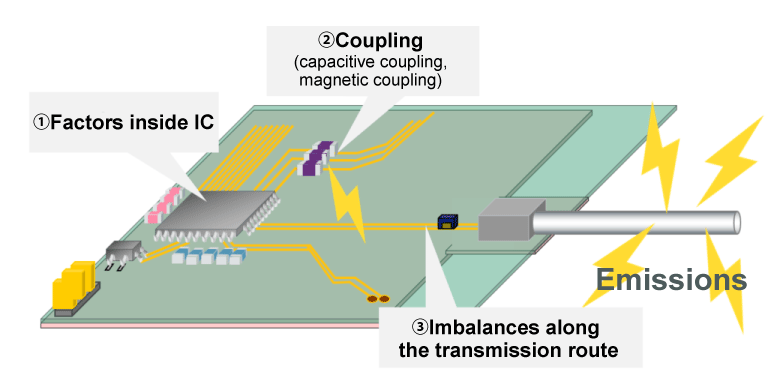
For noise emissions

3. Noise Issues in Automotive Ethernet
In differential transmission lines, where noise does not tend to be generated, noise issues can still occur when a common mode current is generated by a variety of factors.
Common mode current flows due to variety of factors
4. Factors for Generation of Common Mode Noise
One characteristic of differential transmission lines is that, generally, common mode noise is not generated. However, if skew (time difference) or an amplitude difference occurs in the signals between both lines, the signal balance between both lines will be lost, and common mode noise will be generated.
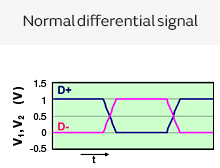
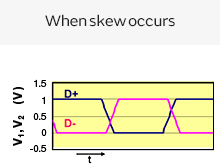
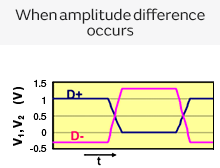
Differential
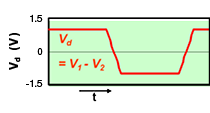
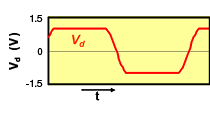
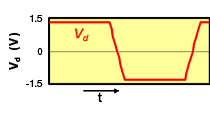
Common
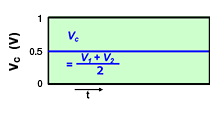
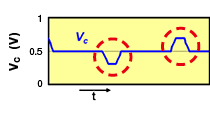
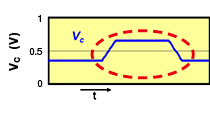
- Continue reading:Noise Suppression Measures for Automotive Ethernet
